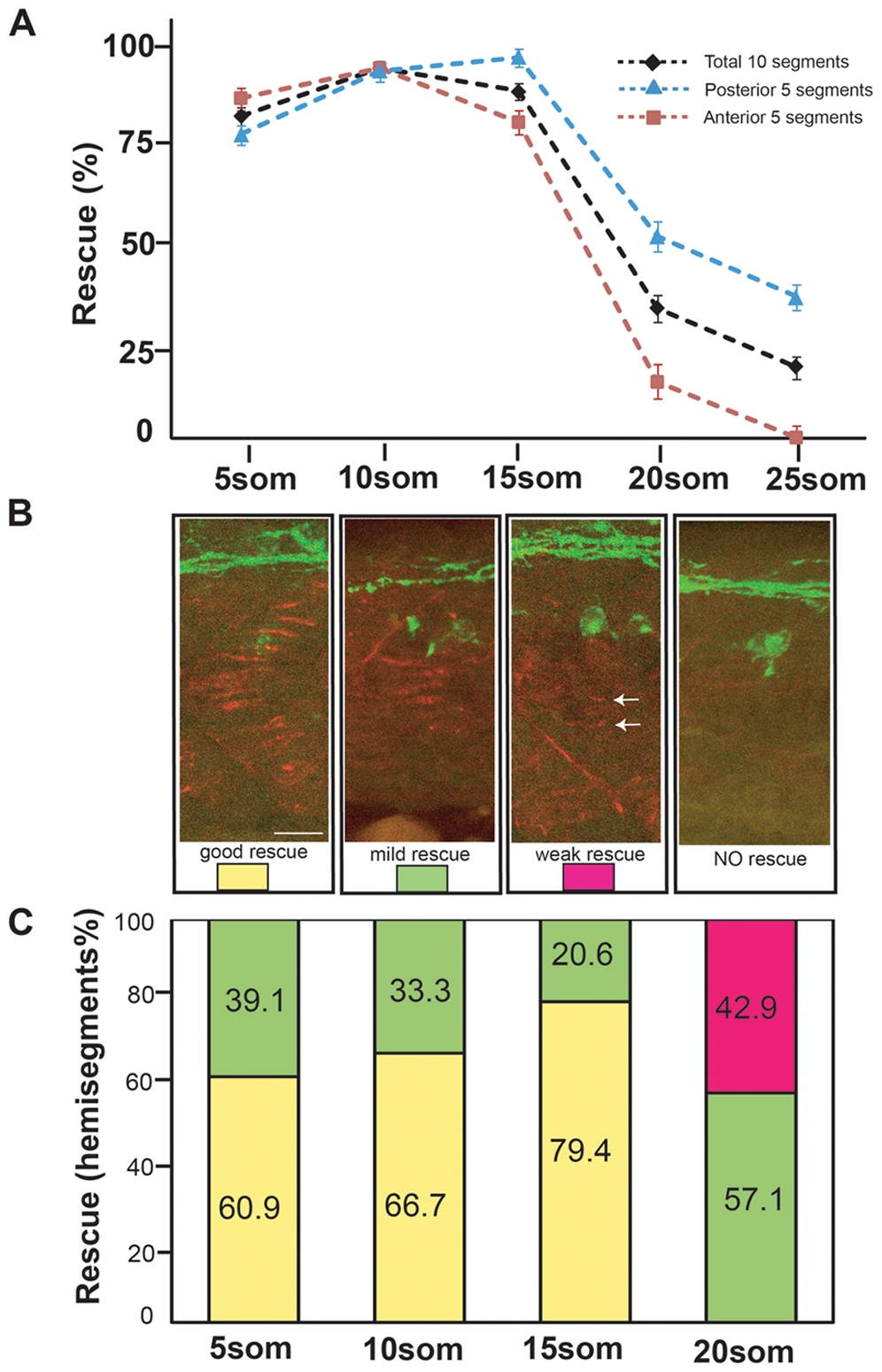
Fig. 3 Rescue of motor axon pathfinding and AChR prepatterning by unplugged/MuSK at different time points.
(A) Temporal series of Tg(hsp70l:unpFLmyc) induction to rescue motor axon guidance. Embryos were heat-shocked starting at the indicated time points and analyzed at 27 hpf. The induction of Tg(hsp70l:unpFLmyc) expression after the 15-somite stage significantly reduced rescue efficacy (segments 6?15, black; segments 6?10, red; segments 11?15, blue). See Materials and Methods for how rescue efficiency was calculated. 20 hemisegments were analyzed in each embryo, and results from multiple experiments are represented as mean±SEM. (n = 644-1028, average = 744, hemisegments per time point). (B and C) Rescue of AChR prepatterning by Tg(hsp70l:unplugged SV1-myc). Embryos were heat-shocked starting at different time points and examined at the 21-somite stage for prepatterned AChR clusters. Only posterior segments (11-15) were analyzed in each embryo (see also Figure S3). (B) Individual hemisegments were scored as ?good rescue? (when AChR clusters were present on most muscles), ?mild rescue? (when AChR clusters formed on <50% of all muscles, mostly around non-migratory adaxial cells), or ?weak rescue? (with smaller prepatterned clusters formed on a few muscles, see arrows). (C) HS treatment of Tg(hsp70l:unplugged SV1-myc) embryos at the 20-somite stage significantly reduced AChR rescue efficacy. Results were summarized from multiple experiments (n = 7-20, average = 13, hemisegments per time point). Scale bar: 20 μM.