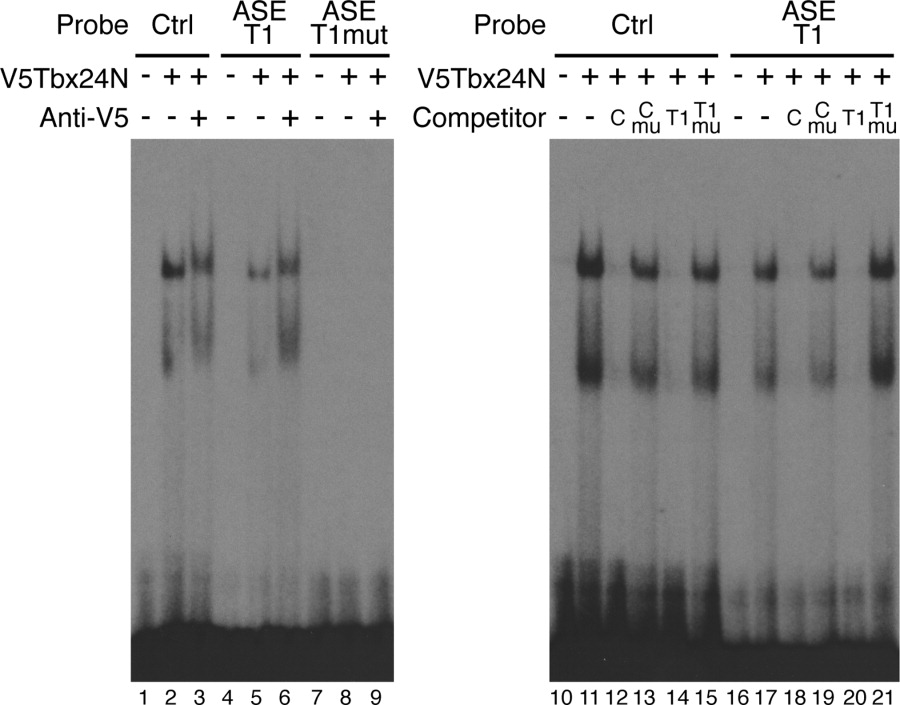
Fig. 3 Identification of a Tbx binding site within the anterior stripe element (ASE). A single Tbx24 binding site in the ASE was confirmed by electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA; lanes 4-6). Control reactions contained unprogrammed lysate (lanes 1, 4, and 7). Tbx24N formed two complexes with the control T-box site and ASE-T1 probe (lanes 2 and 5). The faster migrating band is likely due to a truncated protein product in the in vitro translation reaction (data not shown). Specificity of binding was confirmed by supershifting complexes with an antibody to the V5 epitope (lanes 3 and 6). Mutation of the T-box in the ASE-T1 sequence abolished Tbx24N binding (lanes 7-9). Binding specificity was further confirmed by competition assays (lanes 10-21). Reciprocal competition was observed between the control and ASE-T1 oligonucleotides (lanes 12, 14, 18, and 20). Oligonucleotides containing mutated T-box sites were unable to compete (lanes 13, 15, 19, and 21). competitors were added at 100-fold molar excess.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.