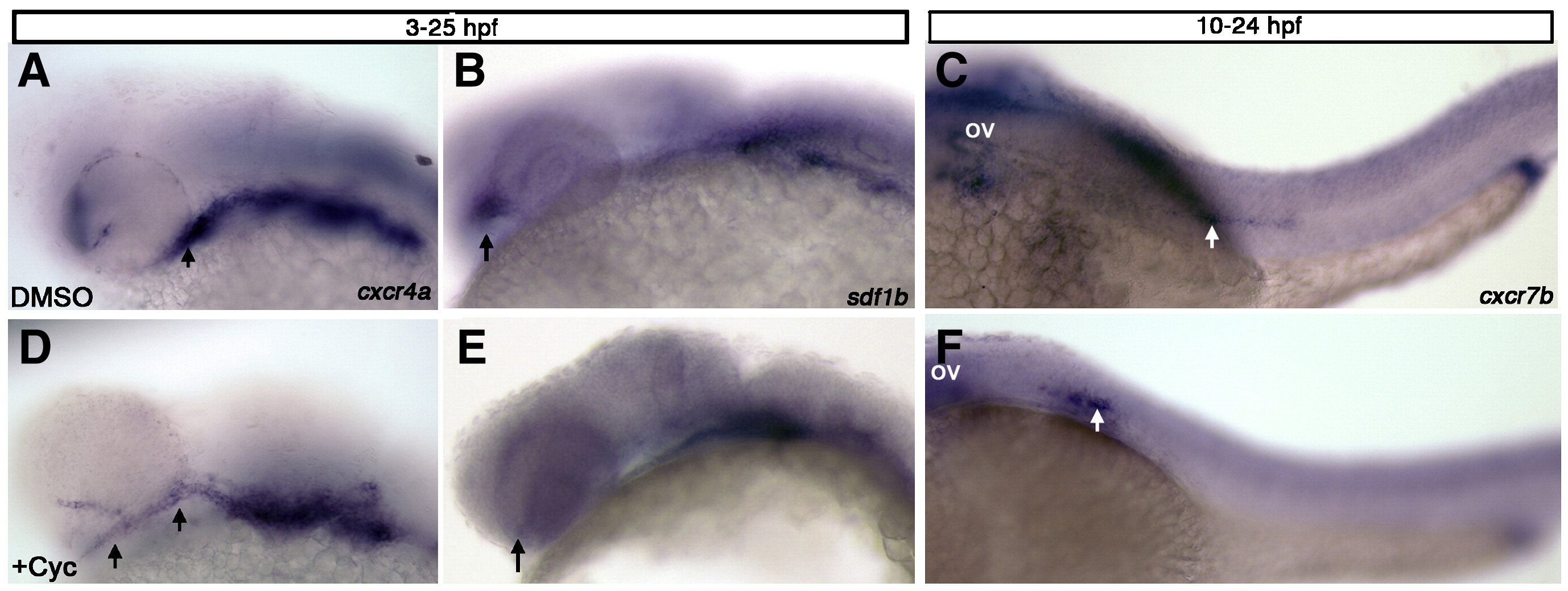
Fig. 7 Hedgehog signaling regulates expression of sdf1b within the optic stalk. Lateral views, anterior to the left observed at 25 hpf (A, B, D, E) and 28 hpf (C, F). (A, B) Embryos treated with DMSO or cyclopamine (D, E) from 3 hpf?25 hpf show mispositioned cxcr4a expression within the optic stalk and less expression in the first arch of cyclopamine treated embryos (D; arrows), as compared to DMSO treated control embryos (A). sdf1b expression in the optic stalk is lost in cyclopamine treated animals (E; arrow) in comparison to DMSO treated controls (B; arrows point to optic stalk in B, E). (C, F) Embryos treated with cyclopamine from 10?24 hpf and observed at 28 hpf with cxcr7b expression show lateral line migration defects. The lateral line primordium in cyclopamine treated embryos (F) does not migrate posteriorly as compared to DMSO treated embryos (C; white arrows). ov, otic vesicle.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 333(1), Olesnicky Killian, E.C., Birkholz, D.A., and Artinger, K.B., A role for chemokine signaling in neural crest cell migration and craniofacial development, 161-172, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.