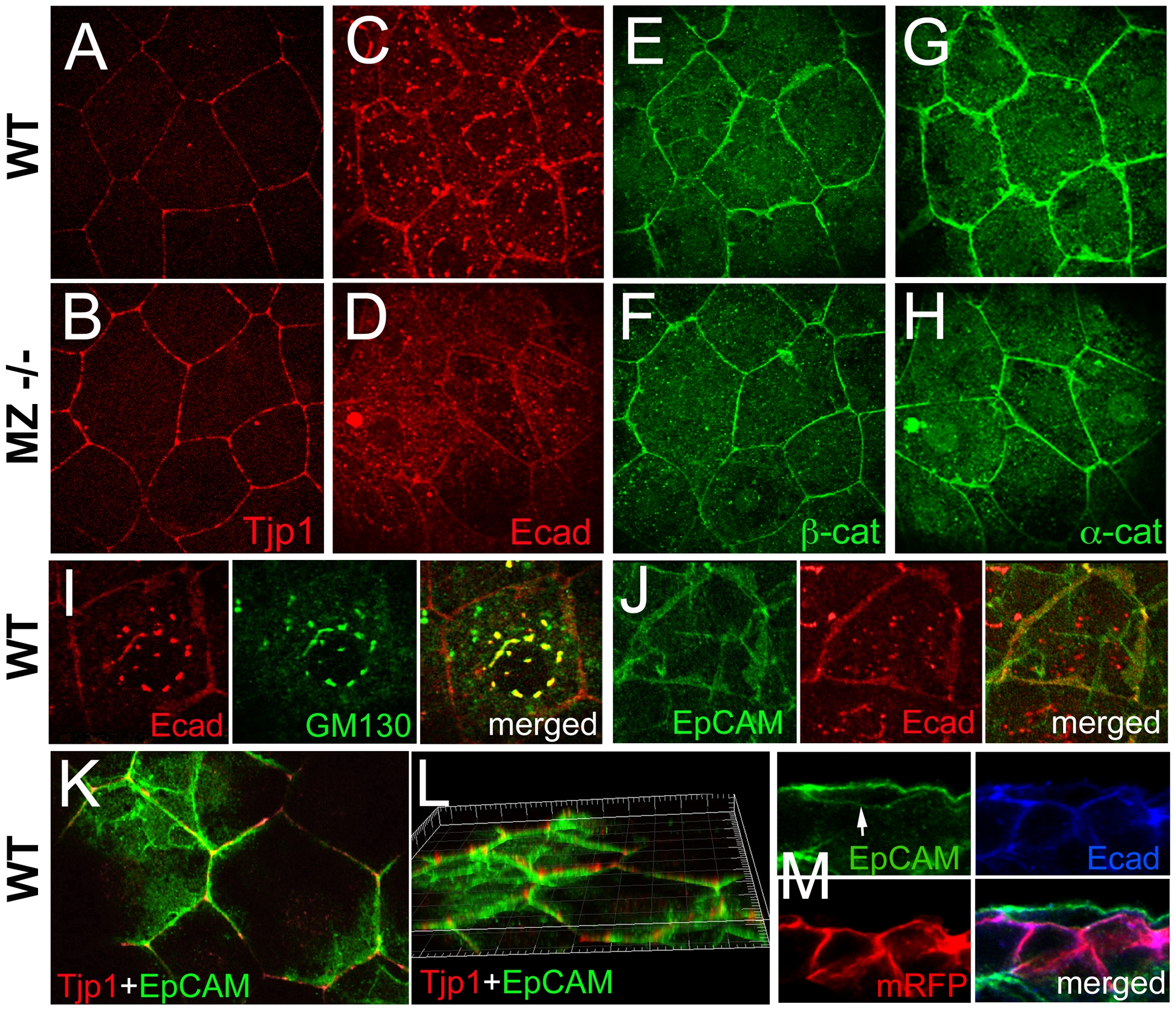
Fig. 8 In wild-type EVL cells, EpCAM is localized at the basolateral membrane and excluded from the apical domain, while the molecular composition of apico-basal membranes is altered in MZepcam mutants.
(A–H) Immunodetection of Tjp1 (A,B), Ecad (C,D), β-catenin (E,F) and α-catenin (G,H) in the EVL of wild-type (A,C,E,G) and MZepcam mutant embryos (B,D,F,H) at 90% epiboly stage. Images were acquired and processed using identical settings for mutant and wild-type samples. Mutants display increased membranous levels of the tight junction protein, but reduced levels of the cadherin-catenin complex. (I–M) Localization studies in wild-type EVL cells at 90% epiboly stage. (I) Double immunodetection of Ecad and the Golgi marker GM130-GFP [80], single and merged channels, revealing perinuclear E-cadherin in the Golgi apparatus. (J) Double immunodetection of Ecad and EpCAM-GFP, single and merged channels, revealing co-localization in a salt-and-pepper-like pattern (compare with [62]). (K,L) Double immunodetection of Tjp1 and EpCAM-GFP, revealing that EpCAM-GFP is localized basal to Tjp1; (L) shows rotated Z-stack. (M) Triple immunodetection of EpCAM-GFP, Ecad and RFP (labeling transplanted deep cells lacking EpCAM-GFP); single and merged channels. The white arrow indicates EpCAM-GFP localized in the basal membrane of the EVL cell (the underlying RFP-positive deep cells lack EpCAM-GFP).