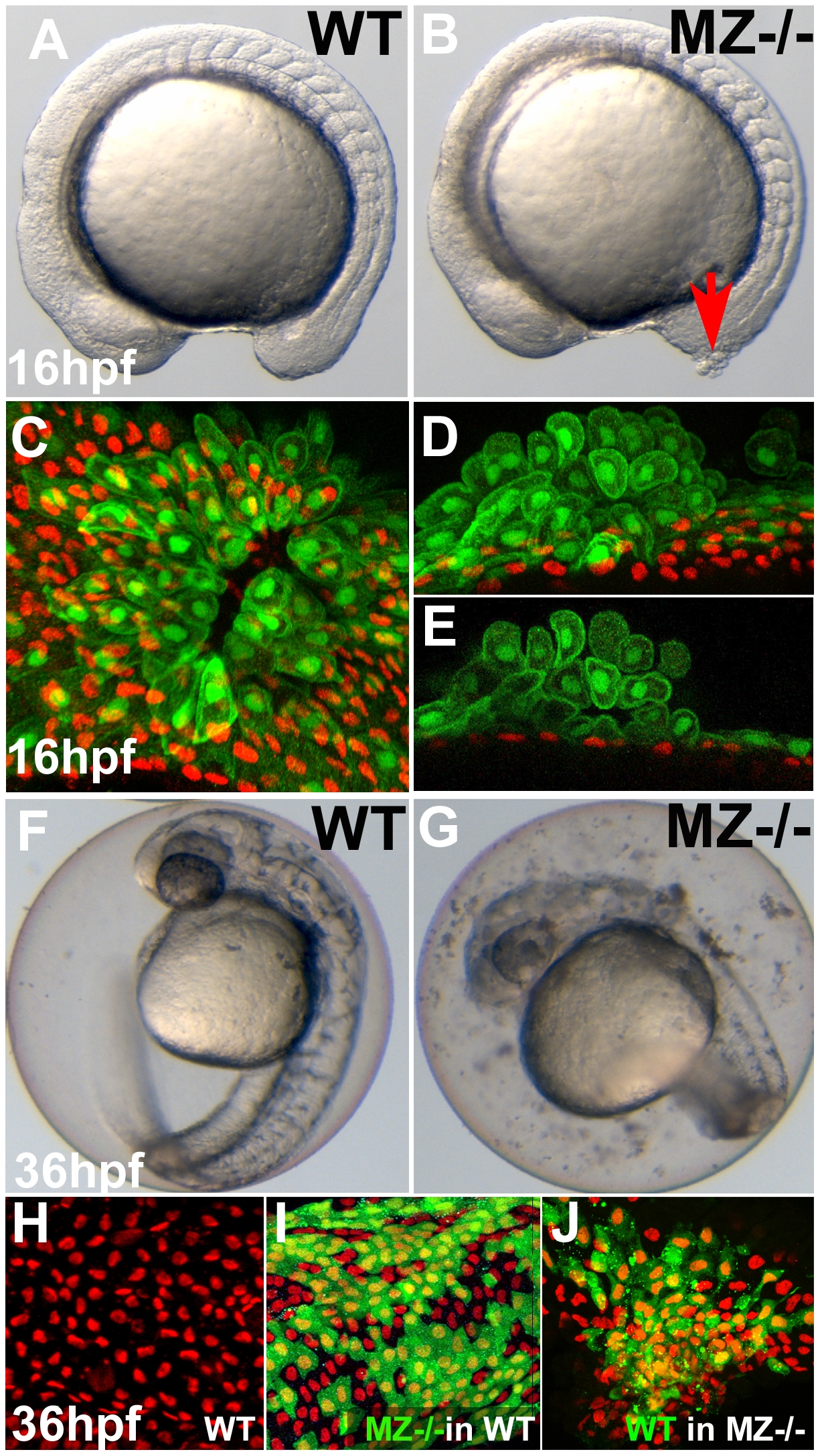
Fig. 3 First cell aggregates of maternal/zygotic epcam mutants are formed during mid segmentation stages, starting in the EVL, whereas basal cell aggregates form secondarily.
(A,B) Maternal/zygotic (MZ) epcam mutant at 16 hpf (12-somite stage) (B) with skin aggregate on tailbud (red arrow). (C?E) Confocal images of skin aggregate at 16 hpf; (C) merged stack of sagittal sections; (D) merged stack and (E) single layer of transverse sections; EVL cells labeled in green (anti-GFP immunostaining of tg(cytokeratin8:GFP) product), nuclei of basal keratinocytes in red (anti-p63 immunostaining). The EVL is ruptured (C), EVL cells have rounded up and have piled up on each other (D,E). In contrast, the underlying basal layer is normally organized, with regularly spaced p63-positive nuclei (D,E). (F,G) Live images of un-hatched embryos at 36 hpf. Sloughed skin cells are present within the chorion of mutant embryo (G). (H?J) Aggregates of basal keratinocytes are formed as a consequence of the loss of EpCAM function in the EVL; stacks of confocal images; transplanted basal cells are stained for GFP in green, nuclei of basal cells for p63 in red. (H) Non-chimeric wild-type control. (I) Chimeric embryo with cluster of MZepcam mutant basal cells (in green) in wild-type environment/underneath wild-type EVL, with normal spatial organization of mutant basal cells. (J) Chimeric embryo with cluster of wild-type basal cells (in green) underneath MZepcam mutant EVL, with aggregations of wild-type basal cells.