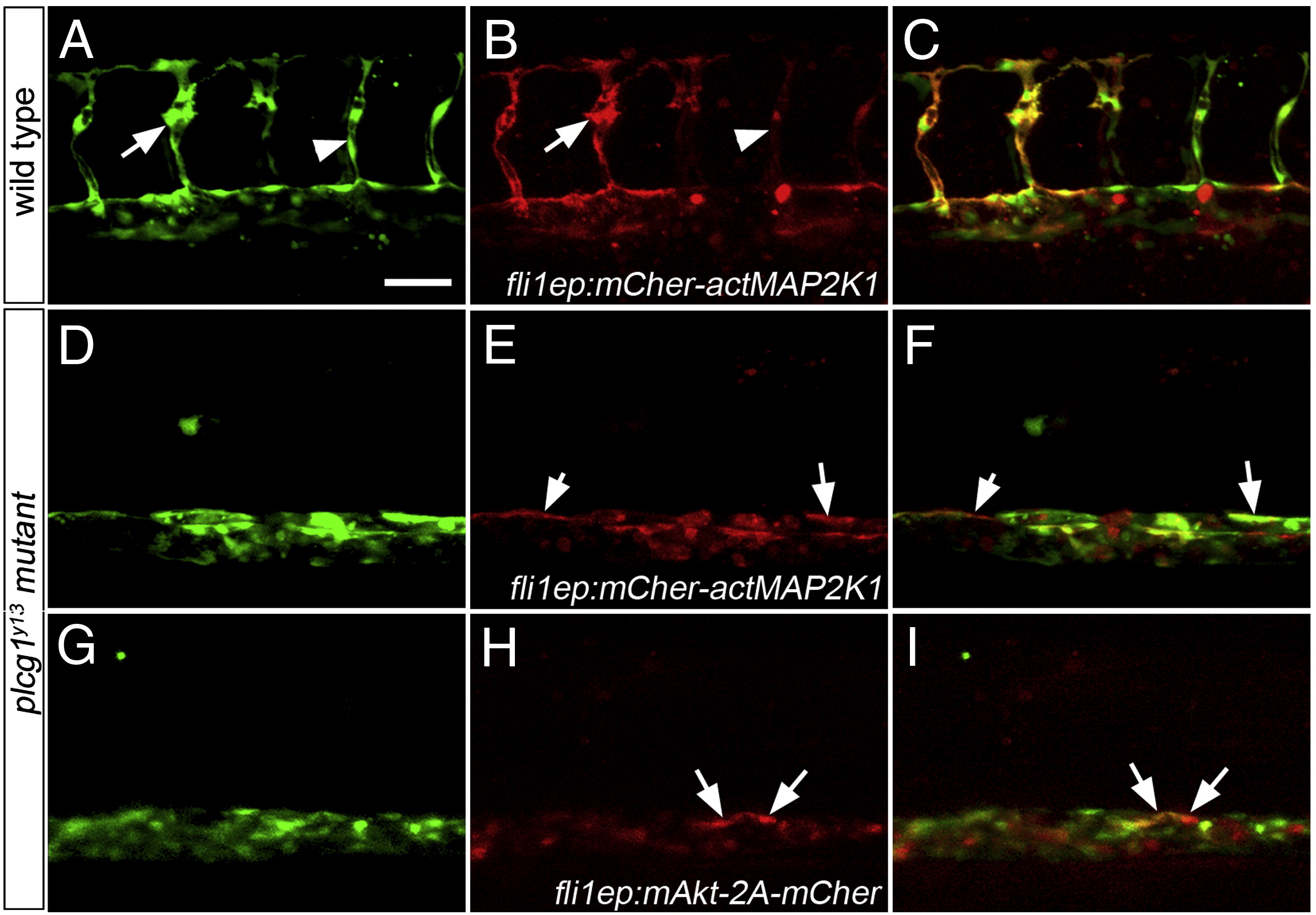
Fig. 5 Activation of Akt or MAPK signaling fails to rescue segmental artery formation in plcg1y13 mutant embryos. (A?I) Confocal fluorescent micrographs of trunk blood vessels at 30 h post fertilization. Anterior is to the left, dorsal is up. Scale bar is 60 μM. (A?C) Wild type Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1 embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mCher-actMAP2K1; arrow denotes excessive filopodial extensions in a sprout expressing high levels of the transgene; arrowhead is a low transgene-expressing cell. (D?F) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1;plcg1y13 mutant embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mCher-actMAP2K1. (E, F) Arrows indicate transgene-expressing cells in the dorsal wall of the aorta. (G?I) Tg(fli1a:egfp)y1;plcg1y13 mutant embryo co-injected with 25 pg Tol2 transposase mRNA and pTol-fli1ep:mAkt-2A-mCher; (H, I) Arrows denote transgene-expressing cells in the dorsal aorta.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 329(2), Covassin, L.D., Siekmann, A.F., Kacergis, M.C., Laver, E., Moore, J.C., Villefranc, J.A., Weinstein, B.M., and Lawson, N.D., A genetic screen for vascular mutants in zebrafish reveals dynamic roles for Vegf/Plcg1 signaling during artery development, 212-226, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.