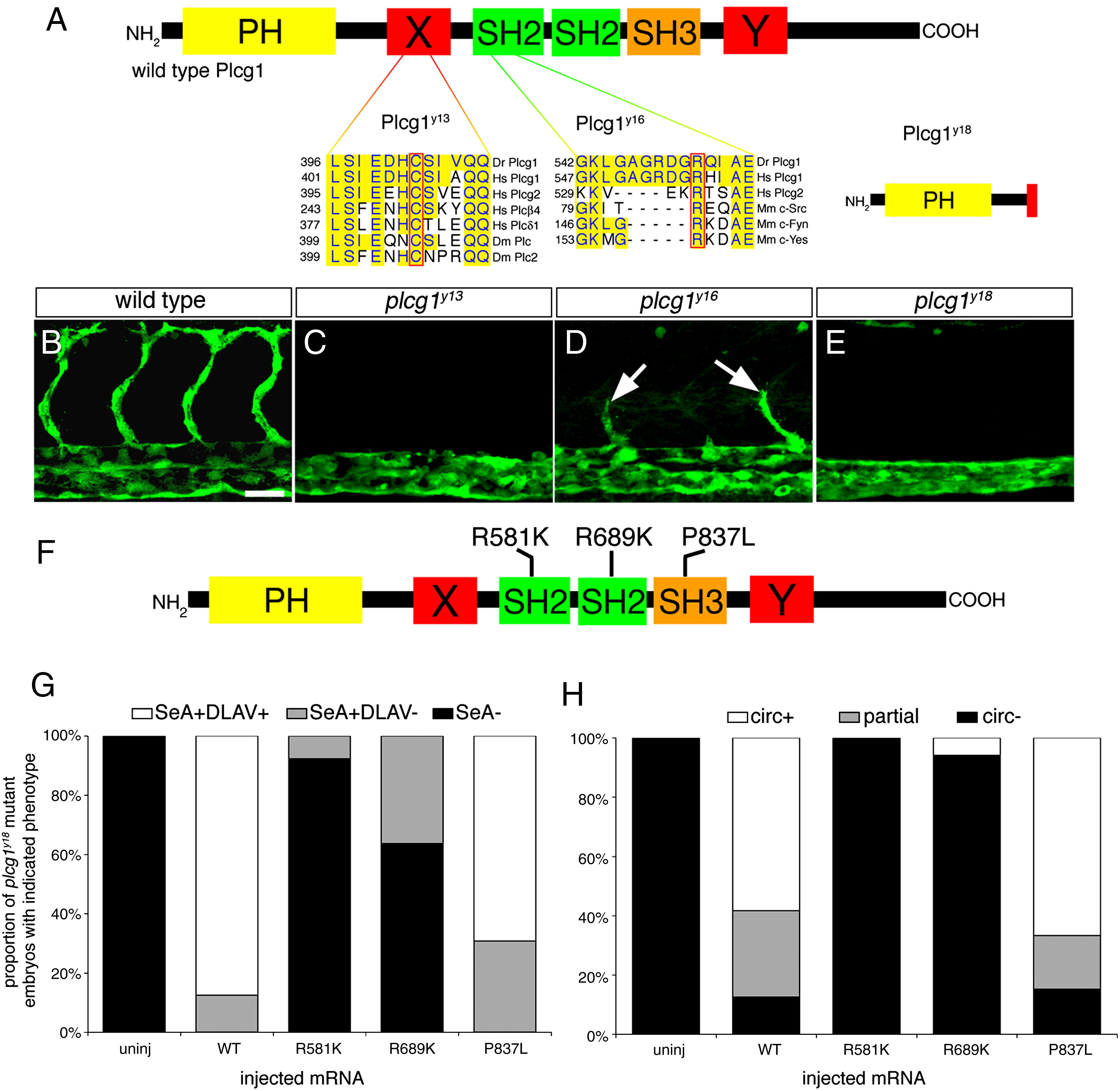
Fig. 4 plcg1 is required for segmental artery formation. (A) Functional domains within Plcg1. PH — pleckstrin homology domain; X, Y — split catalytic domains; SH2 — src homology–2 domains; SH3 — src homology 3 domain. Residues affected by the y13 and y16 mutations are outlined in red and aligned with conserved sequences from other species (Dr — zebrafish, Hs — human, Dm — Drosophila, Mm — mouse). The y18 allele leads to a truncation in the X-catalytic domain. (B–E) Confocal fluorescent micrographs of trunk blood vessels at 30 h post fertilization. Lateral views, anterior to the left, dorsal is up. (B) Wild type sibling embryo. Scale bar is 50 μM. C. Loss of segmental arteries in a plcg1y13 mutant embryo. (D) Partial segmental arteries (white arrows) in a plcg1y16 mutant embryo. (E) plcg1y18 mutant embryo. (F) Position of point mutations engineered into rescue constructs in the Plcg1 SH2 and SH3 domains. (G) Graph indicating proportion of embryos displaying segmental artery or DLAV formation following injection with mRNA encoding the indicated Plcg1 construct. (H) Graph indicating proportion of embryos displaying partial or complete circulation following injection with mRNA encoding the indicated Plcg1 construct; SeA — segmental arteries, DLAV — dorsal longitudinal anastamotic vessel, circ — circulation, partial — shunt between dorsal aorta and posterior cardinal vein.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 329(2), Covassin, L.D., Siekmann, A.F., Kacergis, M.C., Laver, E., Moore, J.C., Villefranc, J.A., Weinstein, B.M., and Lawson, N.D., A genetic screen for vascular mutants in zebrafish reveals dynamic roles for Vegf/Plcg1 signaling during artery development, 212-226, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.