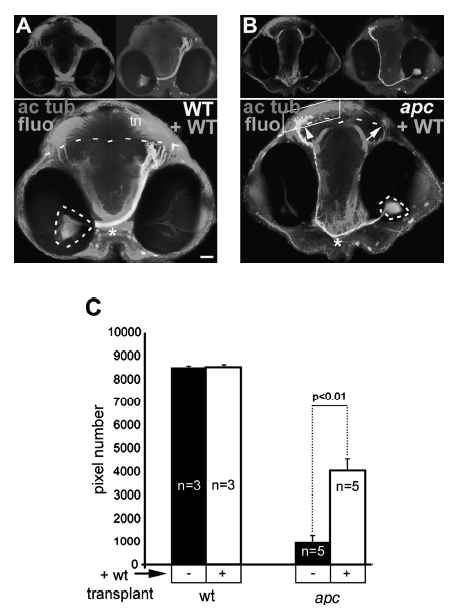
Fig. 4 Axons from transplanted wild-type cells within the apc-/- retina are able to reach the tectum. (A, B) Transplantation of wild-type cells in retina of wild-type (A) or mutant (B) embryos. Frontal view showing location of fluorescein-labeled transplanted wild-type cells (circled with dashed lines) and their axons projecting to tectum (right panel inset) and acetylated tubulin labeling (left panel inset). The boundary between OT and tegmentum is indicated with dashed lines. In mutants (A), wild-type axons are able to cross at the OC (asterisk) and project to the mutant tectum (arrow), similarly to the axons of wild-type cells transplanted into wildtype embryos (arrow). Acetylated tubulin labeling in the OT neuropil is increased. Note the more ventral location of the OC (asterisk) in transplanted mutant versus wild-type embryos. (C) Quantification of acetylated tubulin labeling in tectum neuropil (boxed area in B) shows 4.2-fold increase of the axonal termination zone in apc mutants upon transplantation with wild-type cells into the retina (Student?s t-test p<0.01). Error bars represent standard deviation (SD). tn, Tectal neuropil. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Zebrafish