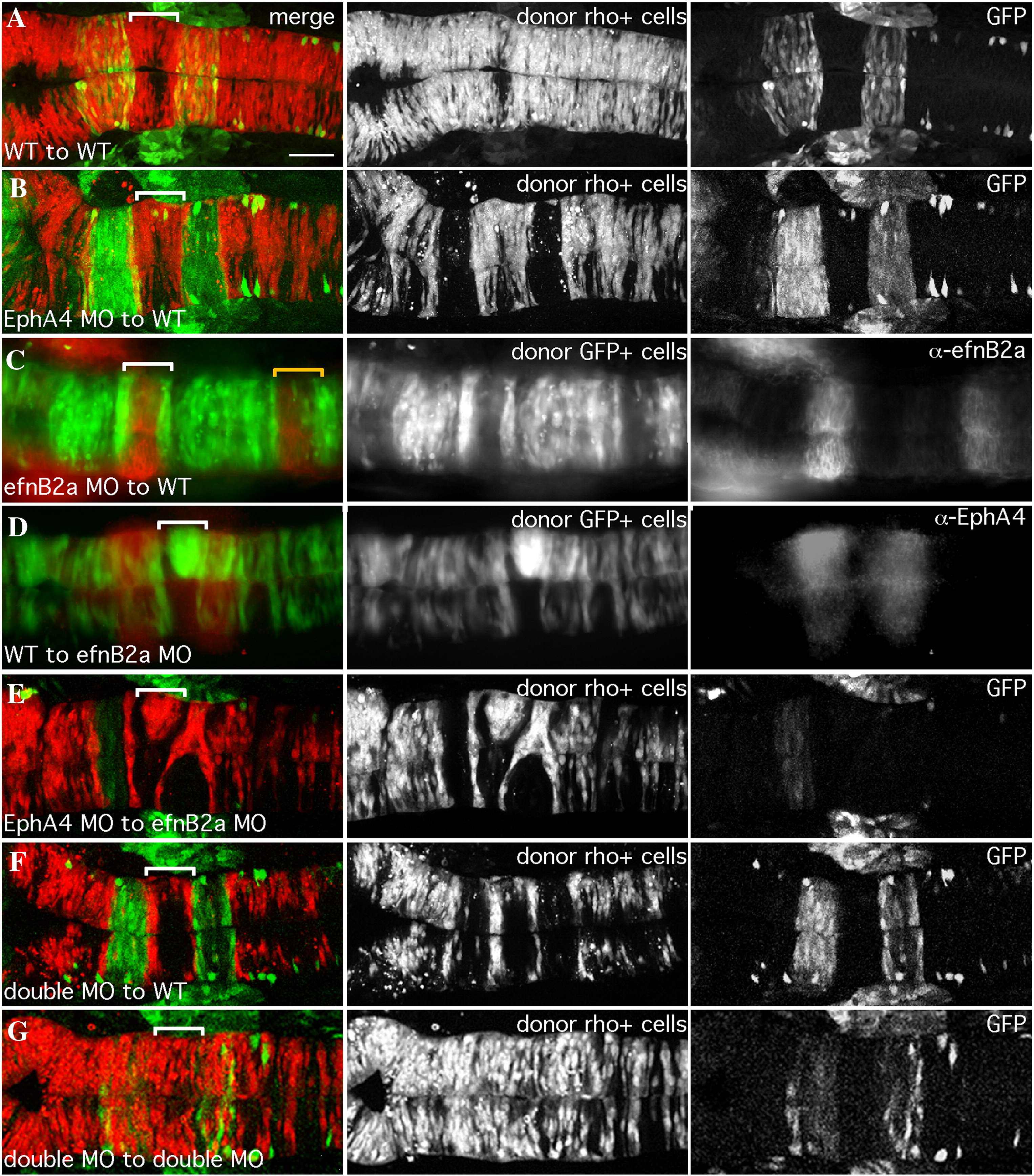
Fig. 1 EfnB2a promotes cell adhesion in r4 independent of EphA4. 18 hpf mosaic embryos shown in dorsal view with anterior to the left. Left panels are merged images of individual channels shown in the middle and right panels. Donor cells (middle panel), are labeled with rhodamine dye (red in the merge; A, B, E, F, G) or express GFP (green in the merge; C, D). Rhombomere-specific markers (right panel): r3 and r5 are identified by expression of GFP in pGFP5.3 transgenic hosts (green in the merge; A, B, E, F, G) or detected by α-EphA4 (red in the merge; D); α-EfnB2a marks r1, r4, r7 (red in the merge; C). r4 is indicated by a white bracket in the merge. (A) WT cells contribute evenly to a WT host hindbrain. (B) EphA4 MO donor cells are excluded from r3 and r5 of a WT host. (C) EfnB2a MO donor cells are excluded from r4 and r7 (yellow bracket) of a WT host embryo. (D) WT donor cells form unilateral clusters on one side of r4 of an EfnB2a MO host. (E) EphA4 MO donor cells are excluded from r3 and r5 and form a unilateral cluster in r4 of an EfnB2a MO host embryo. (F) EfnB2a; EphA4 double MO donor cells are excluded from r3, r4, and r5 of WT host embryos. (G) EphA4; EfnB2a double MO donor cells contribute homogeneously to the hindbrain of a double MO host embryo. Scale bar: 50 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 327(2), Kemp, H.A., Cooke, J.E., and Moens, C.B., EphA4 and EfnB2a maintain rhombomere coherence by independently regulating intercalation of progenitor cells in the zebrafish neural keel, 313-326, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.