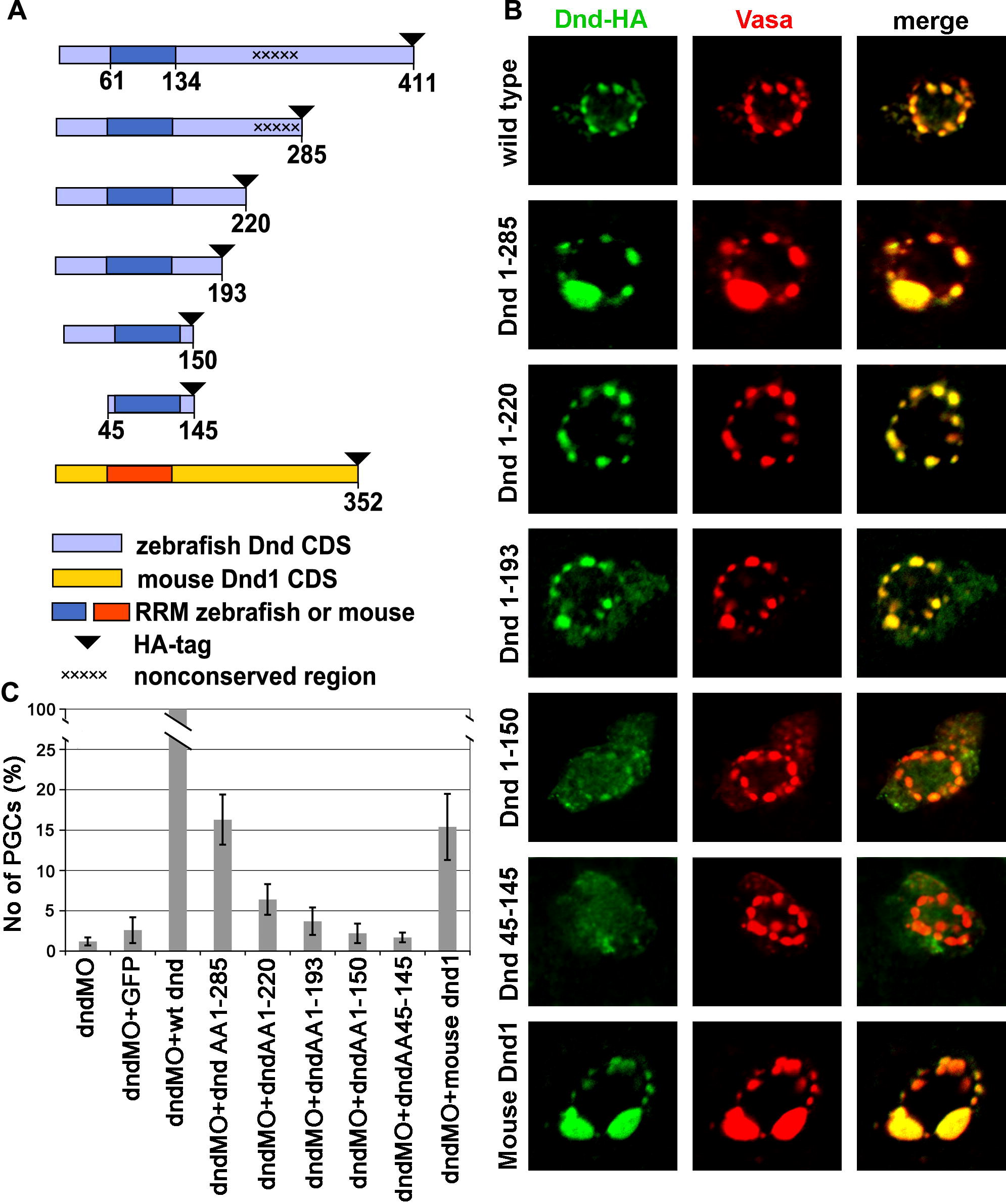
Fig. 2 Deletions of parts of Dead end protein reveal domains important for protein localization and function. (A) Schematic drawing of Dead end deletion constructs. (B) Intracellular localization of the various Dnd-deletion fusion proteins detected by immunohistochemistry with anti-HA antibody (Green) in comparison with the position of the GCGs reported by anti-vasa antibody staining (Red). (C) A chart depicting the ability of the various deletions constructs to supplement for wild type Dead end. The values represent the number of rescued PGCs in embryos co-injected with a specific Dnd truncated protein and dnd MO, normalized to the PGCs rescued by a wild type dnd mRNA injection (see the text for details).
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 126(3-4), Slanchev, K., Stebler, J., Goudarzi, M., Cojocaru, V., Weidinger, G., and Raz, E., Control of Dead end localization and activity ? Implications for the function of the protein in antagonizing miRNA function, 270-277, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.