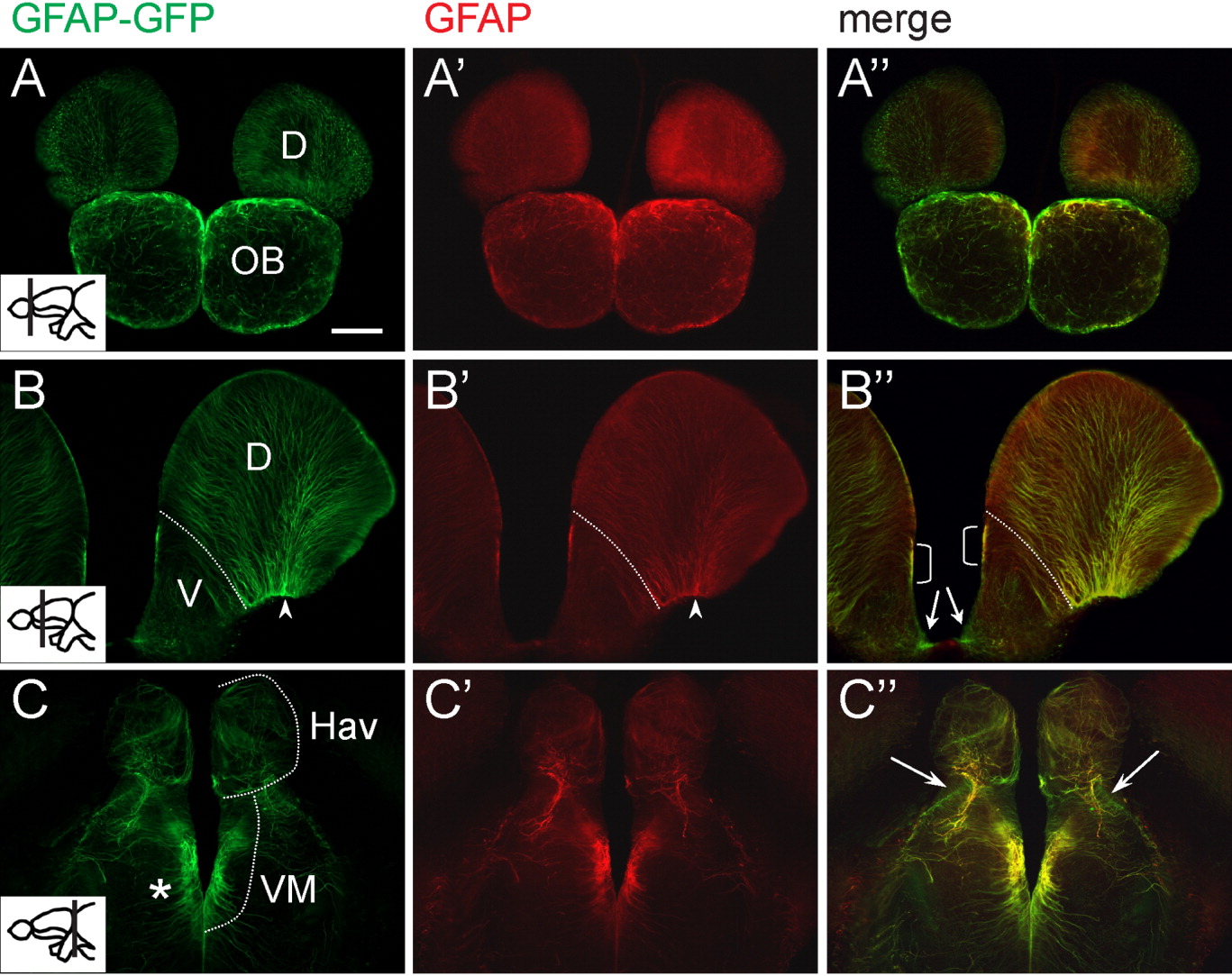
Fig. 1 Comparison of tg[GFAP-GFP] and endogenous glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) expression in the forebrain of adult zebrafish. A-C′: Vibratome sections were stained with anti-green fluorescent protein (GFP; A-C) and anti-GFAP (A′-C′) antibodies. A″-C″: The merged channel shows overlapping signals in most regions, except for subtle differences at the periphery of the central nervous system (indicated by arrows). In the dorsal telencephalon, radial fibers coexpressing GFP and GFAP converge at the basal side (arrowhead in B,B′). Dotted line in B,B′ delineates the boundary between the dorsal and ventral telencephalon. Bracketed region in B″ indicate a domain that correlates with previously identified region for fast-proliferating cells. Asterisk in C shows GFP- and GFAP-positive radial fibers in the diencephalon. Plane of section is indicated in the inset of A-C. Images were acquired with a compound microscope. D, dorsal telencephalic area; Hav, ventral habenular nucleus; OB, olfactory bulb; V, ventral telencephalic area; VM, ventromedial thalamic nucleus. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.