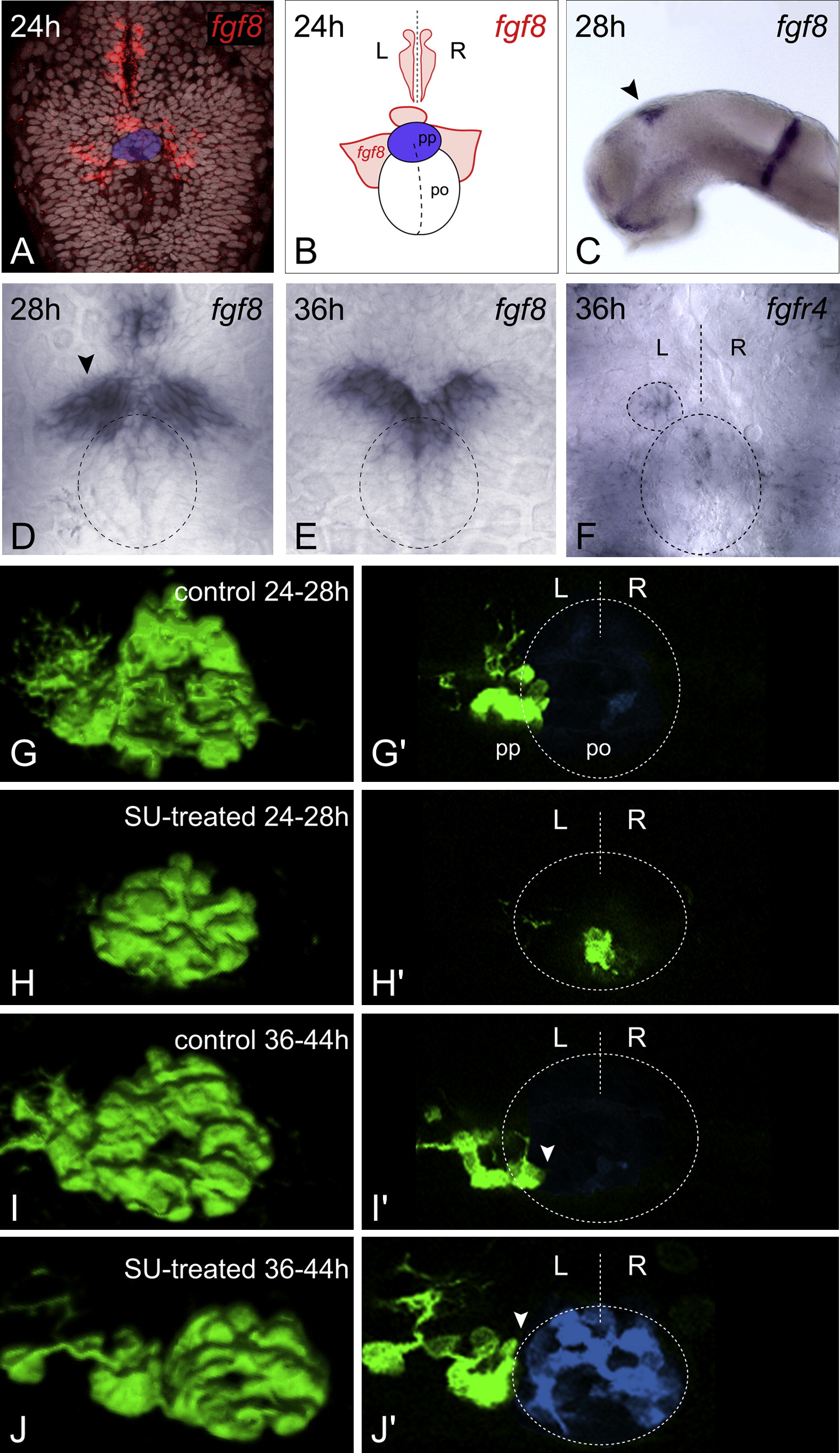
Fig. 2 Temporally Controlled Abrogation of Fgf Signaling Identifies a Critical Window for Fgf-Dependent Parapineal Migration
(A and C?E) Expression of fgf8 in the epithalamus at 24 hpf ([A], dorsal view, TOPRO3 nuclear marker in gray, parapineal primordium highlighted in blue), 28 hpf ([C], lateral, black arrowhead; [D], dorsal, black arrowhead denotes stronger left-sided expression), and 36 hpf ([E], dorsal). Dashed ellipse indicates position of pineal nucleus (D and E). (B) Schematic depicting pineal organ (po), parapineal nucleus (pp, blue), fgf8 expression domains (red), and midline (dashed line), as visualized in (A). (F) fgfR4 expression at 36 hpf (dorsal). Dashed lines indicate position of pineal nucleus (large ellipse), parapineal nucleus (small ellipse), and midline (straight line). (G?J) 3D reconstructions and (G′?J′) single z-slices of dorsal views of the epithalamus in control- (G, G′, I, and I′) and SU5402- (H, H′, J, and J′) treated Tg(foxD3:GFP) 4 dpf embryos, with anterior to the top. Pineal cells have been pseudocolored in blue in single z-slices and dashed lines indicate position of pineal nucleus and midline (G′?J′). SU5402 treatment at 24?28 hpf completely abolished the initial leftward migration of the parapineal to lateral and dorsal positions (H, and H′). Treatment at 36?44 hpf abrogated later translocation of the parapineal to ventral and medial locations relative to the pineal nucleus, and parapineal cells remain at dorso-lateral positions adjacent to the pineal ([J and J′], white arrowheads). L, left; R, right.