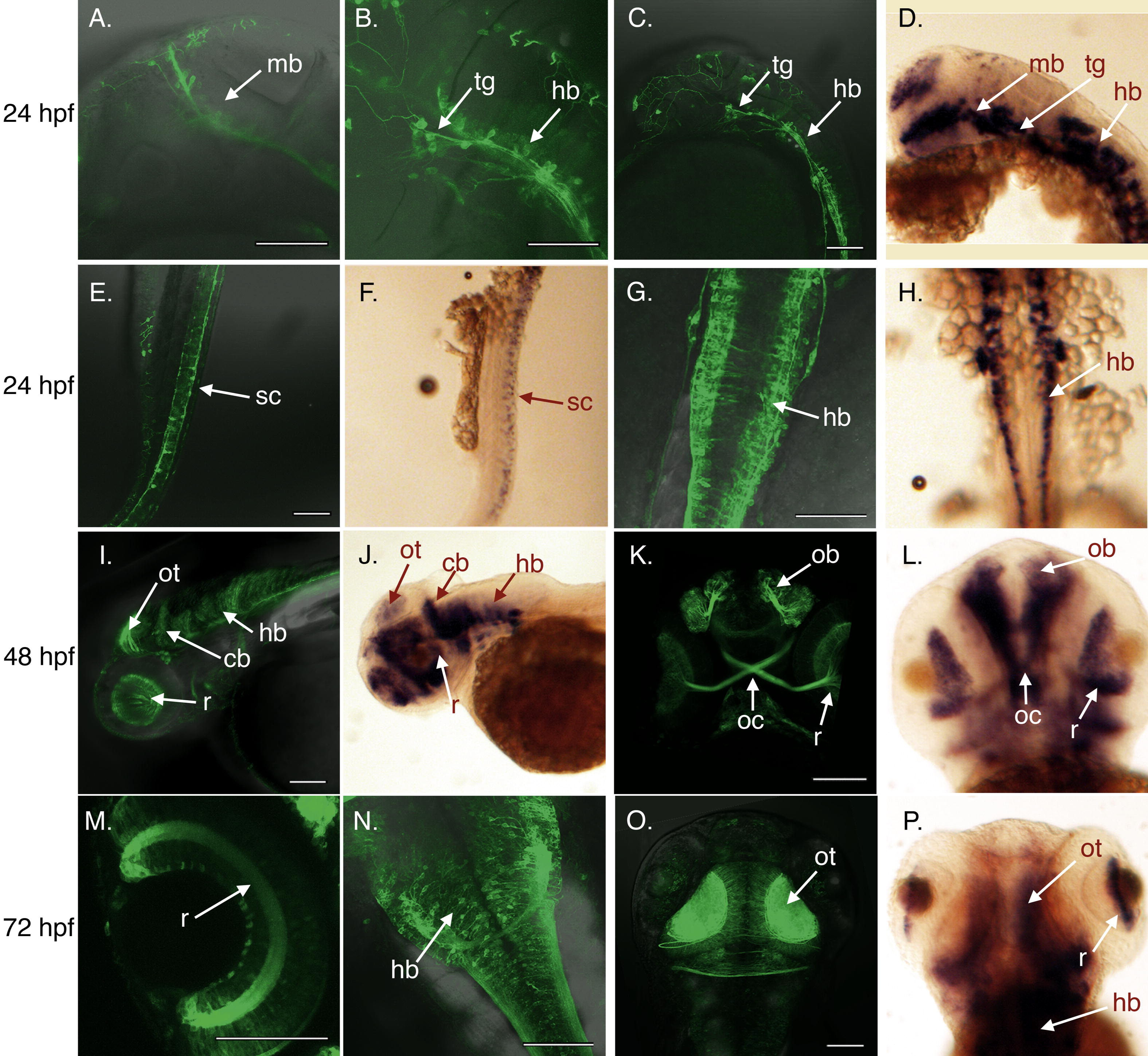
Fig. 4 Fugu gap43 promoter mimics endogenous gap43 expression pattern in developing embryos. (A–C, E, and G) Neurons from 24 hpf tg(3.6fgap43:GFP)SA1 embryos expressing GFP in the midbrain (mb) and hind brain (hb), as well as neurons in the trigeminal ganglion (tg), and spinal cord (sc). Expression of endogenous gap43 determined by in situ hybridization show similar patterns of expression (D, F, H). 48 hpf: expression in the retina(r), cerebellum (cb), hindbrain (hb), olfactory bulb (ob), optic chiasm (oc), optic tectum (ot) observed for transgene (I, K) and endogenous gap43 (J, L). 72 hpf: expression in the retina (r), hindbrain (hb), optic tectum (ot) observed for transgene (M–O) and endogenous gap43 (P). (A–F, I, J) lateral views; (G, H, M–P) dorsal views; (K, L) ventral views. Scale bars = 100 μm.
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 8(6), Udvadia, A.J., 3.6kb Genomic sequence from Takifugu capable of promoting axon growth-associated gene expression in developing and regenerating zebrafish neurons, 382-388, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns