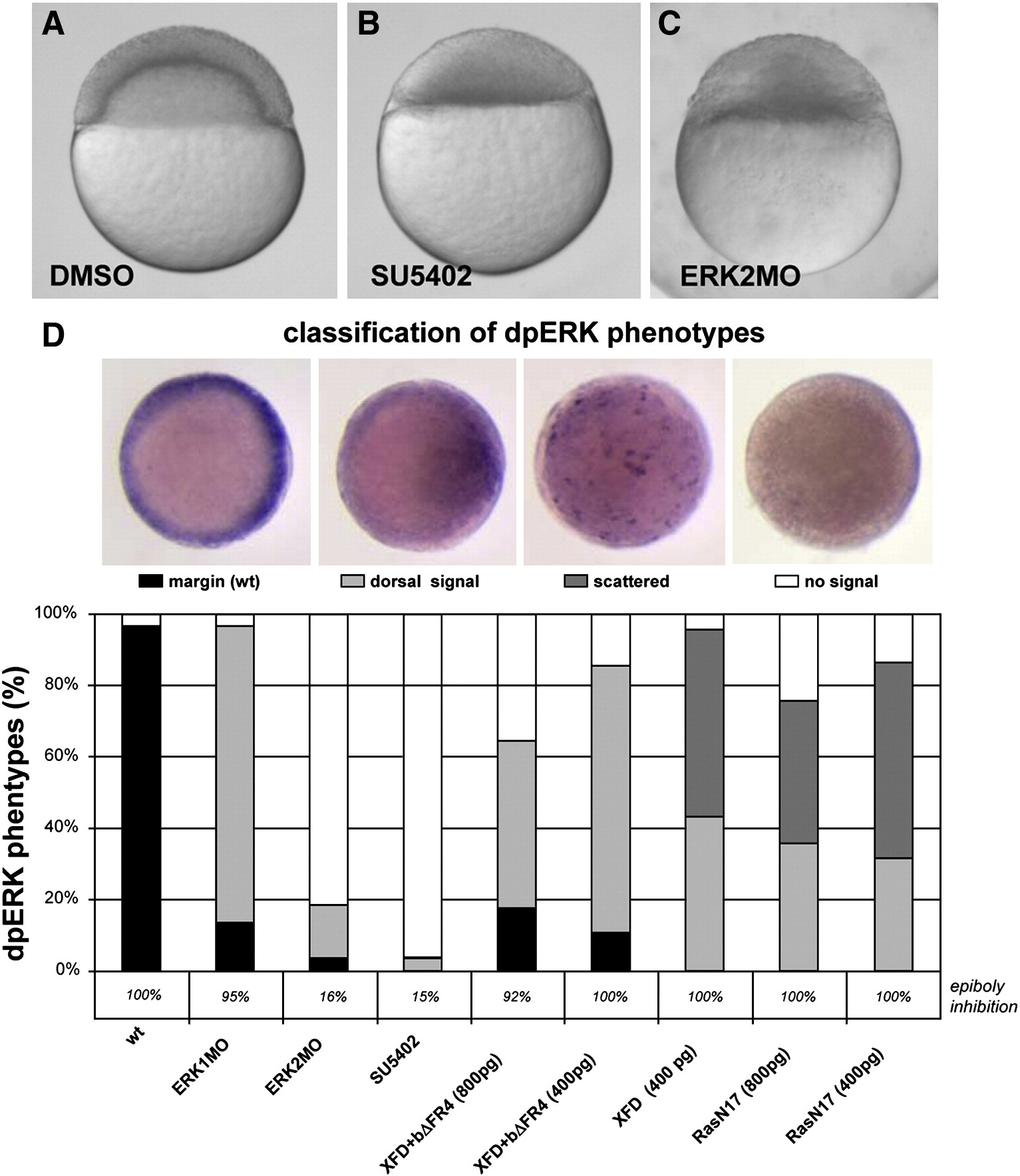
Fig. 8 Chemical inhibition of FGF signaling phenocopies ERK2MO affects and prevents epiboly initiation. Representative embryos treated with DMSO (A), SU5402 (B) or injected with ERK2MO (C). Both SU5402 (40 μM) treated and ERK2 depleted embryos do not initiate epiboly, whereas (co-)injections of synthetic mRNA encoding XFD and bΔFR4 (800 or 400 pg total, ratio 1:1), XFD only (400 pg) or Ras N17 (800 or 400 pg) did not affect epiboly initiation significantly (D; percentages indicated below the graph). (D) Injected or SU5402 treated embryos were analyzed for active ERK signaling (dpERK) after the mentioned treatment, at 4 hpf. The observed dpERK phenotypes were imaged from the top and classified in 4 groups; staining in the margin like in wild type conditions (wt; black), depletion of dpERK from the margin, but still present at the putative dorsal side (dorsal signal; light gray), no signal in the margin, but scattered pattern of cells expressing dpERK (scattered; dark gray) and no signal detected (white). The different phenotypes were scored per treatment and the percentages were plotted in a graph (D).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 319(2), Krens, S.F., He, S., Lamers, G.E., Meijer, A.H., Bakkers, J., Schmidt, T., Spaink, H.P., and Snaar-Jagalska, B.E., Distinct functions for ERK1 and ERK2 in cell migration processes during zebrafish gastrulation, 370-383, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.