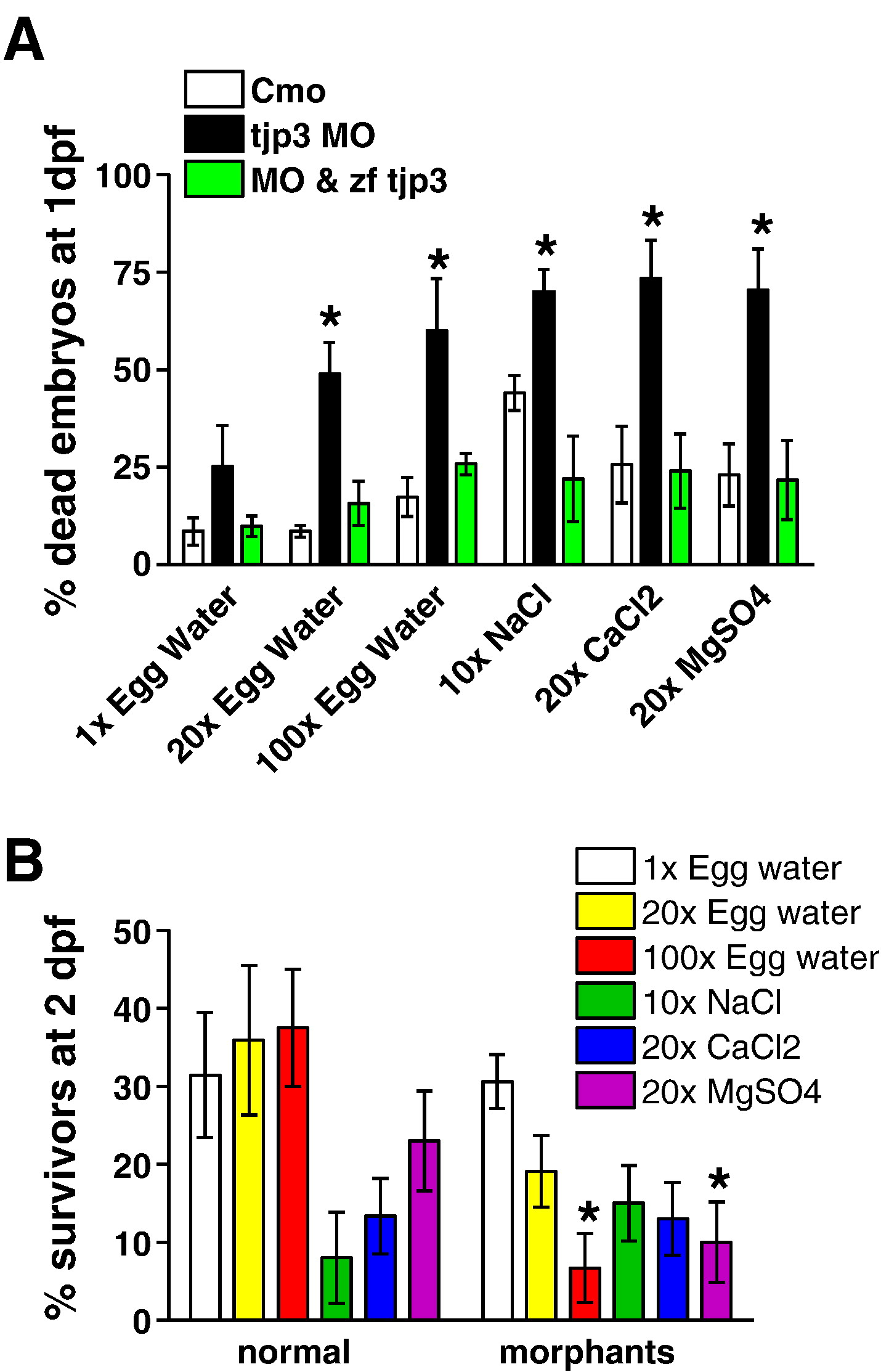
Fig. 9 Tjp3/zo-3 morphants are sensitive to osmotic stress. (A) The ability of tjp3/zo-3 morphants to survive high salt conditions is significantly reduced compared to control or rescued embryos. Embryos were either injected with control morpholino or tjp3/zo-3 splice morpholino or they were rescued by coinjecting MO with pcDNA3.1 containing zebrafish tjp3/zo-3 (MO & zf tjp3). Embryos were dechorionized and exposed to high salt conditions (see Materials and methods) at 6 hpf. Surviving embryos were counted at 1 dpf. A significant fraction of tjp3/zo-3 morpholino injected embryos died prematurely compared to control embryos. Mean and S.E.M.; n ≥ 20 per experiment; 3?5 independent experiments. t-test; p < 0.05. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. (B) Selection against tjp3/zo-3 morphants exposed to high salt or high magnesium during embryogenesis. High sodium and calcium salt concentrations reduced the survival of both normal (no phenotype) and morphant embryos. However, in 100x egg water and in 20x MgSO4 the number of morphants that survived to 2 dpf was significantly lower than that of normal embryos. Mean and S.E.M.; n ≥ 20 per experiment; 3?5 independent experiments. 2-way ANOVA; p < 0.05; statistical significance is indicated by asterisks.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 316(1), Kiener, T.K., Selptsova-Friedrich, I., and Hunziker, W., Tjp3/zo-3 is critical for epidermal barrier function in zebrafish embryos, 36-49, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.