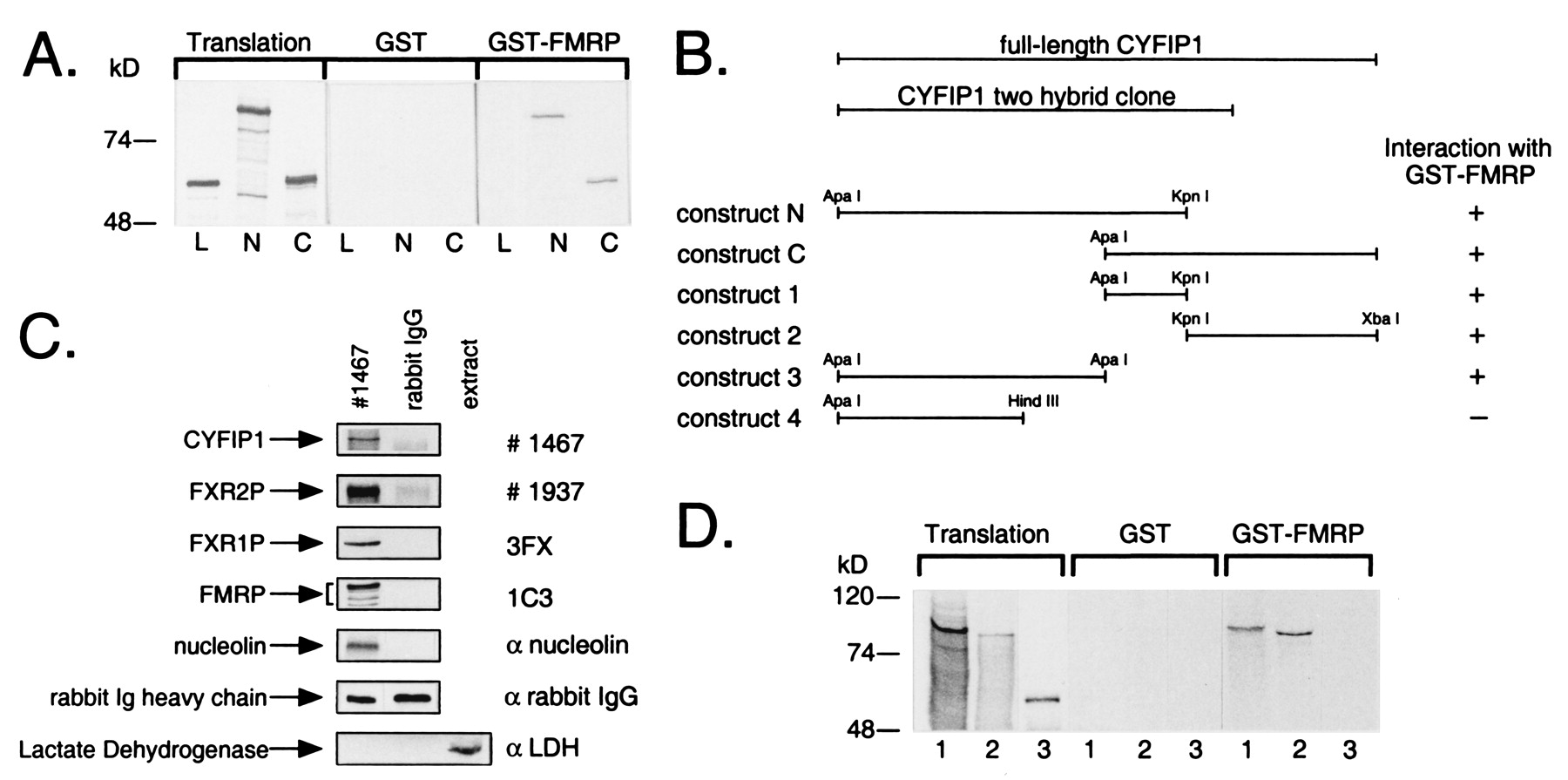
Fig. 1 FMRP interacts with CYFIP1/2. (A) Interaction in vitro between GST-tagged full-length FMRP and in vitro translated CYFIP1 N and C terminus (N, C), overlapping by 184 amino acids. GST-pd assays were performed in the presence of 100 mM sodium chloride. In each lane, 10% of the translation product used in each reaction or 40% of the eluate from glutathione beads was loaded. Both overlapping parts of CYFIP1 were retained by GST-FMRP but not by GST alone. Luciferase (L), the negative control, was bound neither by GST-FMRP nor by GST alone. (B) GST-pd assays using additional truncated constructs of CYFIP1 revealed that the N + C overlapping region is not exclusively responsible for interaction with FMRP. No binding affinity to GST-FMRP has been shown by construct 4 (amino acids 1-416). (C) Interaction of CYFIP1 with FMRP in vivo. FMRP, FXR1P, FXR2P, and nucleolin were coimmunoprecipitated from cytoplasmic lysate of HeLa cells by 8 μg of pAb no. 1467 raised against CYFIP1. A functional unrelated protein, lactate dehydrogenase, was not precipitated but was present in the cytoplasmic extract (lane 3). None of the proteins was precipitated by the same amounts of rabbit IgG, demonstrating the specificity of the experiment. One percent of each coimmunoprecipitation reaction was loaded to reveal CYFIP1 and the rabbit IgG heavy chain, eight percent to reveal coprecipitated proteins. (D) CYFIP2 is interacting with GST-FMRP in vitro. CYFIP1 translation product (amino acids 1-959, lane 1) and CYFIP2 translation product (amino acids 1-890, lane 2) were retained by GST-FMRP, but not the negative control (luciferase, lane 3). Assay and loading were performed as described in A. Proteins were separated in 8 or 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA