Fig. 3
Targeted Gene Knockdown of Stra6 Causes Embryonic Abnormalities and Vitamin A Deficiency in Developing Eyes
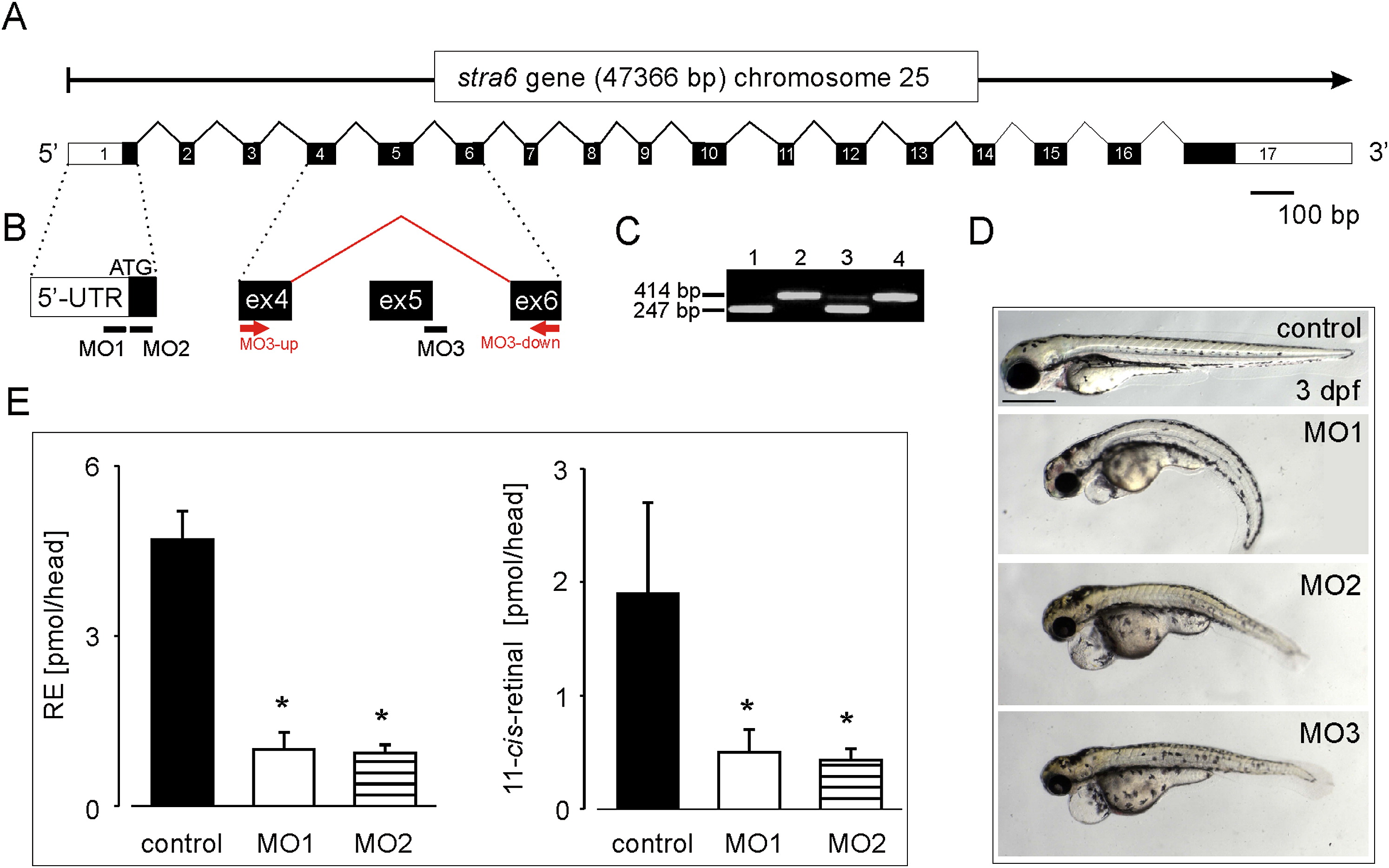
(A) Schematic structure of the zebrafish stra6 gene. White boxes indicate the 5′- and 3′-primed untranslated regions (UTRs), and black boxes represent the coding regions of the stra6 mRNA.
(B) Morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) binding sites directed against the stra6 mRNA. Binding of MO1 and MO2 blocks translation of the stra6 mRNA. For the deletion of exon 5, MO3 is targeted to the exon 5 splice donor site of the stra6 pre-mRNA.
(C) RT-PCR analysis with exon 5-spanning primers MO3-up and MO3-down (see [B]) confirms the deletion of exon 5 in MO3-treated morphants. Lane 1, MO3-treated embryo with developmental defects (see [D]); lane 2, control embryo; lane 3, MO3-treated embryo without severe developmental defects; lane 4, control embryo.
(D) Photographs of 3 dpf control and characteristic stra6 morphant larvae injected with MO1, MO2, and MO3, respectively.
(E) Retinyl esters (RE) and 11-cis-retinal levels in the heads of 4 dpf MO1 and MO2 morphants as compared to control larvae. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.005 versus control by Student′s t test.
Reprinted from Cell Metabolism, 7(3), Isken, A., Golczak, M., Oberhauser, V., Hunzelmann, S., Driever, W., Imanishi, Y., Palczewski, K., and von Lintig, J., RBP4 Disrupts Vitamin A Uptake Homeostasis in a STRA6-Deficient Animal Model for Matthew-Wood Syndrome, 258-268, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell Metab.