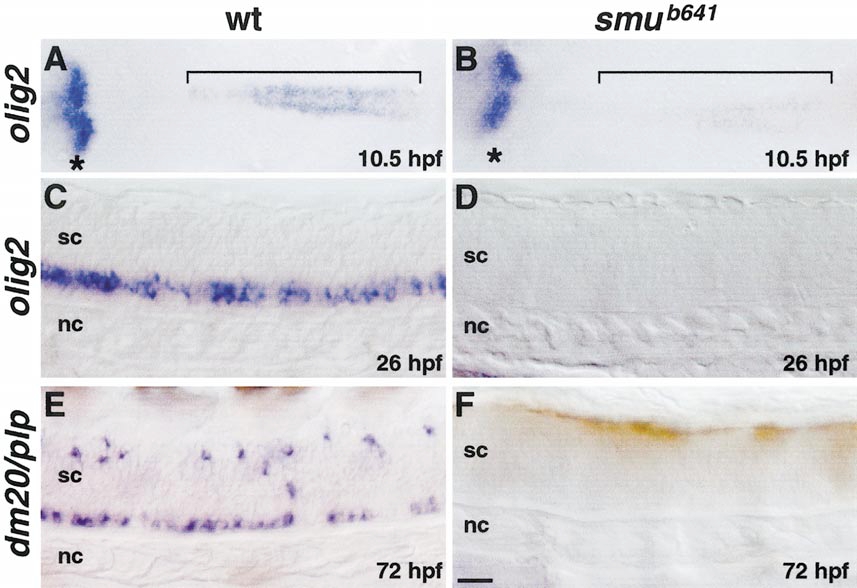
Fig. 7 Hedgehog signaling is required for olig2 expression and oligodendrocyte development. (A, B) Dorsal views, anterior to the left, of flat-mounted embryos hybridized with olig2 probe. Brackets indicate olig2 expression in prospective spinal cord cells. smu mutant embryos express olig2 at a much lower level (B) compared with wild type (A). Asterisks mark olig2 expression in prospective ventral diencephelon, which appears normal in mutant embryos. (C, D) Side views of 26-hpf embryos, anterior to the left. Spinal cord cells of smu mutant embryos do not express olig2. (E, F) Side views of 72-hpf embryos, anterior to the left. Spinal cord oligodendrocytes, marked by dm20/plp expression, do not develop in smu mutant embryos. Scale bar, 40 μm (A and B) and 20 μm (C?F).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 248(2), Park, H.-C., Mehta, A., Richardson, J.S., and Appel, B., olig2 is required for zebrafish primary motor neuron and oligodendrocyte development, 356-368, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.