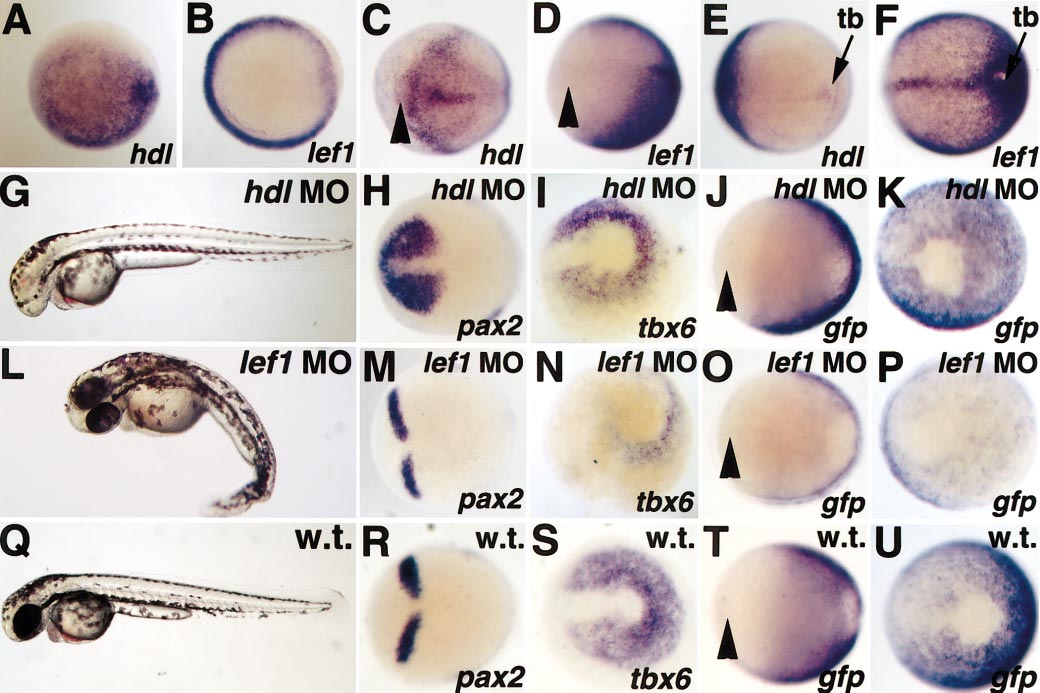
Fig. 2 Reporter expression requires lef1, but not hdl, activity. Animal pole views are shown in (A) and (B). Anterior views with dorsal to the right are shown in (C, D, H, J, M, O, R, T). Posterior views with dorsal to the left are shown in (E, F, I, K, N, P, S, U). Arrowheads mark the rostral limit of the neurectoderm. At shield stage, hdl is expressed throughout the epiblast (A), while lef1 is expressed primarily in the germ ring (B), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to Fig. 1B). At bud stage, hdl is expressed in the anterior neurectoderm and underlying prechordal plate (C), while lef1 expression is absent in this region (D), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to T). hdl is expressed very weakly in the tailbud (tb) at bud stage (E), while lef1 is expressed at high levels in this region (F), similar to TOPdGFP (compare to U). Injection of a hdl morpholino phenocopies the hdl mutant at 36 hpf, causing loss of telencephalon and eyes (G). The hdl morpholino results in rostral expansion of pax2 (compare H and R), but has no effect on tbx6 expression (compare I and S). Loss of hdl has no effect on expression of TOPdGFP in the anterior neurectoderm (compare J and T) or in the tailbud (compare K and U). Injection of a lef1 morpholino results in loss of tail structures posterior to the yolk extension at 36 hpf (L). While the lef1 morpholino has no effect on pax2 expression (compare M and R), it significantly decreases tbx6 (compare N and S). Similarly, loss of lef1 has no effect on anterior TOPdGFP expression (compare O and T), but it significantly decreases expression in the tailbud (compare P and U).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 241(2), Dorsky, R.I., Sheldahl, L.C., and Moon, R.T., A transgenic Lef1/beta-catenin-dependent reporter is expressed in spatially restricted domains throughout zebrafish development, 229-237, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.