Fig. S3
Cell Non-Autonomous Requirement of Smoothened Function in the Induction of Dorsal Pancreatic Endocrine Cells
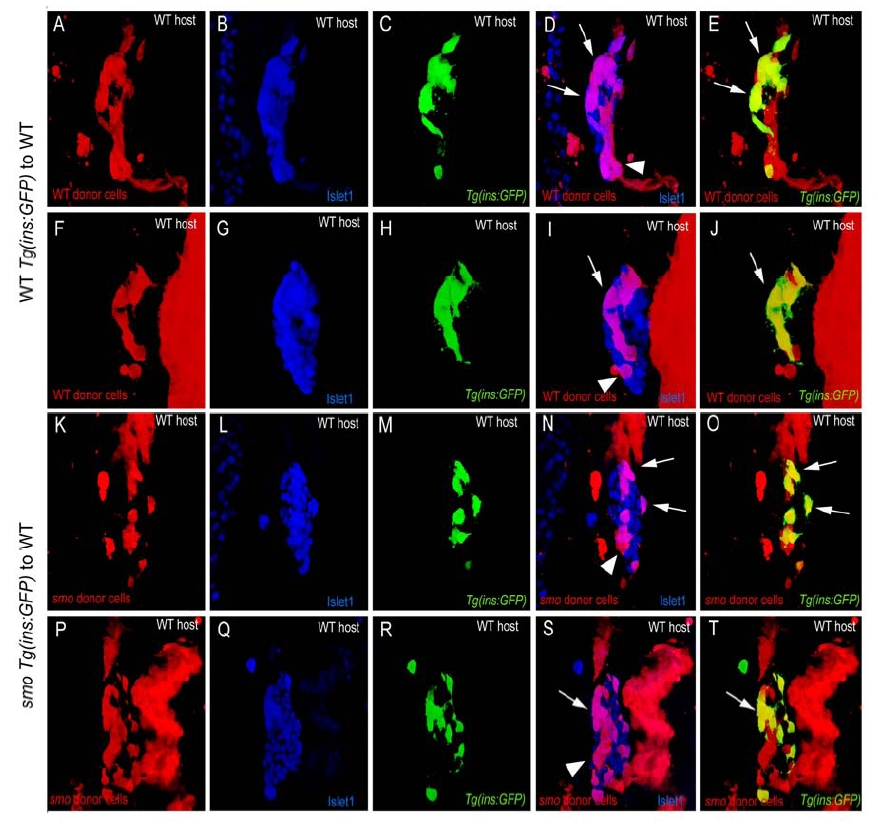
(A-T) Confocal projections of wildtype hosts with wildtype (A-J) and smo mutant (K-T) Tg(ins:GFP) donor cells at 30 hpf. Hosts were stained for Islet1 (blue; B, G, L and Q), which marks all pancreatic endocrine cells, and GFP (green; C, H, M and R). All donor cells are labeled with rhodamine dextran (red; A, F, K and P). [(D), (I), (N) and (S)] represent merged views of [(A), (F), (K) and (P)] and [(B), (G), (L) and (Q)] respectively. [(E), (J), (O) and (T)] represent merged views of [(A), (F), (K) and (P)] and [(C), (H), (M) and (R)] respectively. (A-E, F-J, K-O and P-T) show the same embryos. Only donor cells can express the ins:GFP transgene. (A-J) Wildtype donor cells (A and F) differentiate into Islet1 positive endocrine cells (D and I; arrows and arrowhead). (E and J) Many of the donor cells co-express the ins:GFP transgene (arrows). (K-T) smo mutant donor cells (K and P) also differentiate into Islet1 positive endocrine cells (N and S; arrows and arrowhead). (O and T) Many of the smo mutant donor cells co-express the ins:GFP transgene (arrows).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 14(4), Chung, W.S., and Stainier, D.Y., Intra-endodermal interactions are required for pancreatic beta cell induction, 582-593, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell