Fig. S2
Hedgehog Signaling Is Required during Gastrulation for Inducing Dorsal Pancreatic β-Cells
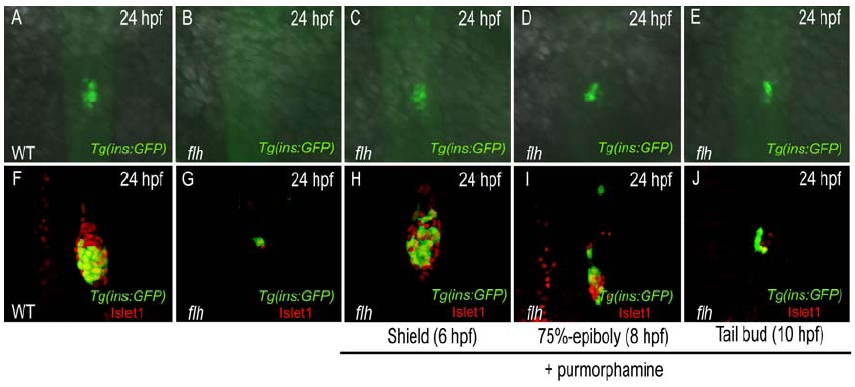
(A-J) Dorsal views (A-E) and confocal projections (F-J) of 24 hpf wildtype (A and F) and flh mutant embryos untreated (B and G) or treated with 20 μM purmorphamine starting at 6 (C and H), 8 (D and I) and 10 (E and J) hpf. Embryos were stained for GFP (A-J) and Islet1 (F-J). (A and F) wildtype embryos show one cluster of Tg(ins:GFP) and Islet1 expressing cells. (B and G) Untreated flh mutant embryos show at most two pancreatic endocrine cells. (C and H) Purmorphamine treatment of flh mutant embryos starting at 6 hpf (shield stage) fully restored Tg(ins:GFP) and Islet1 expression, comparable to wildtype (A and F). (D-E and I-J) Purmorphamine treatment of flh mutant embryos starting at 8 (75%-epiboly stage; D and I) or 10 (tail bud stage; E and J) hpf partially restored Tg(ins:GFP) and Islet1 expression, and with decreasing efficiency as the drug was added at later time points during gastrulation.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 14(4), Chung, W.S., and Stainier, D.Y., Intra-endodermal interactions are required for pancreatic beta cell induction, 582-593, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell