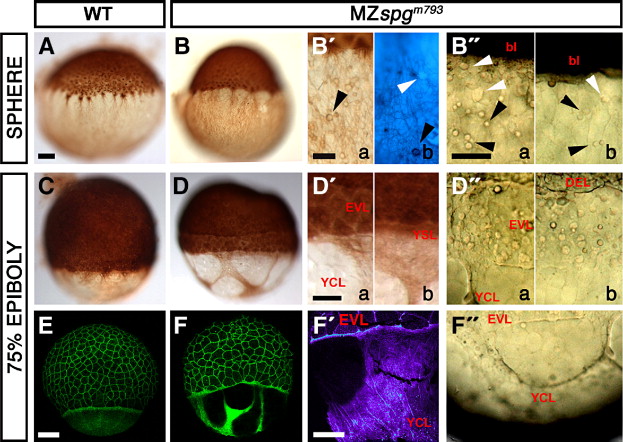
Fig. 3 Distorted yolk cell cortical layer integrity. (A?D, B′, D′) Anti-β-Tubulin/DAB staining of the cortical Tubulin network in MZspgm793 and WT embryos, as indicated. (B2b) Combined Höchst33342/anti-β-Tubulin-antibody/DAB stainings of MZspgm793 embryos showing small spheres (arrowheads) located within the cortical layer of non-nuclear origin. (B″) Small cortical spheres (arrowheads) in a living MZspgm793 embryo. (C, D) Shield stage. (D) Formation of a gap between DEL and EVL in MZspgm793 embryos. (D, D′) Anti-Tubulin stained embryos reveal cortical layer distortions with areas that appear devoid of a cytoplasmic layer. (D″, F″) Cortical layer distortions in living MZspgm793 embryos (arrowhead). (E, F) Confocal z-projections of Alexa488-Phalloidin stained embryos visualize Actin filament distribution. (F) Distortions of the punctuate band and the continuous Actin deposition in the YCL in MZspgm793 embryos. (F′) Color depth-coded projection of confocal image stack. Subpanels in panels B2, B″, D′, and D″: (a) strong, (b) mild phenotypes. bl: blastoderm, EVL: enveloping layer, DEL: deep cell layer, YCL: yolk cytoplasmic layer, YSL: yolk syncytial layer. Scale bar: 100 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 315(1), Lachnit, M., Kur, E., and Driever, W., Alterations of the cytoskeleton in all three embryonic lineages contribute to the epiboly defect of Pou5f1/Oct4 deficient MZspg zebrafish embryos, 1-17, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.