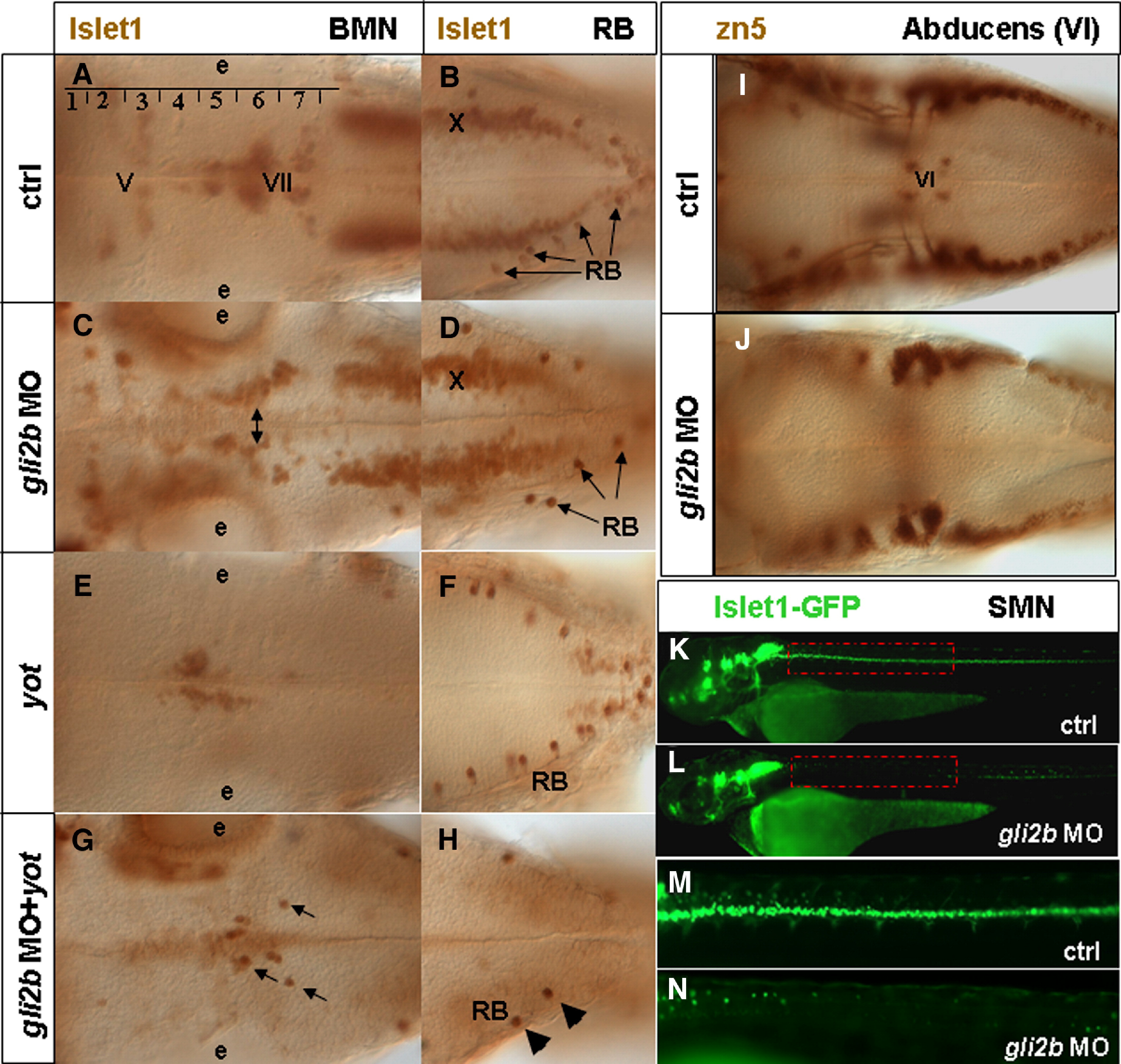
Fig. 5 Gli2/Gli2b and cell differentiation. (A) Islet1-positive branchiomotor neurons (BMNs) and (B) RBs in 48 hpf wild-type embryos. Rhombomeres are numbered in Arabic. The motor nuclei of cranial nerves numbers are in Roman as follows: V, trigeminal; VI, abducens; VII, facial; X, vagal. (C) In Gli2b morphants the motor nuclei (in particular, the facial one, two-headed arrow) were further away from the ventral midline. (D) In Gli2b morphants the RBs were slightly reduced. (E) BMNs and (F) RBs in yot-/- mutant. The trigeminal and vagal motor nuclei are absent. Cell migration of the facial nucleus from rhombomere 4 to rhombomeres 6, 7 is affected (E). No major change in distribution of RBs was found in yot-/-. (G) The residual cells of facial nucleus of yot-/- were reduced even further after injection of gli2b MO while some that remain (arrows) migrated to rhombomeres 6, 7, and the number of RBs (arrowheads) was largely reduced (H). (I) The abducens nucleus (VI) labeled with zn5 antibody in 48 hpf wild-type embryos. These cells were lost in Gli2b morphants (J). (K, L) Position-related changes of motor neurons in controls (K) and Gli2b morphants (L). (M, N) Blow-up of the mid-trunk region indicated by the red line in panels K and L. Abbreviations: e, ear.
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 37(2), Ke, Z., Kondrichin, I., Gong, Z., and Korzh, V., Combined activity of the two Gli2 genes of zebrafish play a major role in Hedgehog signaling during zebrafish neurodevelopment, 388-401, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.