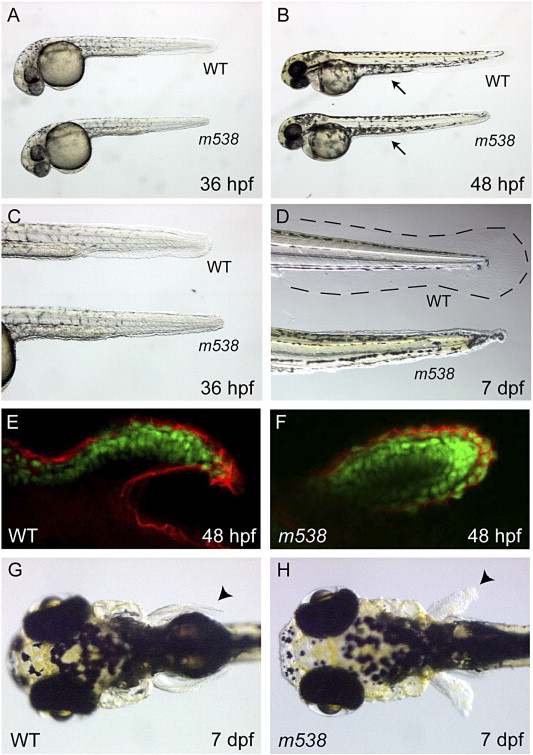
Fig. 1 m538 mutants have severe fin and yolk extension defects. (A–D) Reductions in median fins are shown at 36 hpf (A, C), 48 hpf (B) and 7 dpf (D). In panel D, the dotted line shows the outer limit of the wild-type fin fold. Mutants often contain reduced or absent yolk extensions (B, arrows). (E–H) Anterior tissues develop normally in the mutants, with the exception of the pectoral fins. Defects in pectoral fin outgrowth can be detected at 48 hpf by immunostaining with a pan-cadherin antibody (red, E, F; green are nuclei stained with DAPI and pseudo-colored green for contrast). At 7 dpf, pectoral fins are short and stunted in m538 mutants (arrowheads in panels G and H). (A–F) Lateral views and (G, H) dorsal views; anterior view is to the left in all images.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 311(2), Webb, A.E., Sanderford, J., Frank, D., Talbot, W.S., Driever, W., and Kimelman, D., Laminin alpha5 is essential for the formation of the zebrafish fins, 369-382, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.