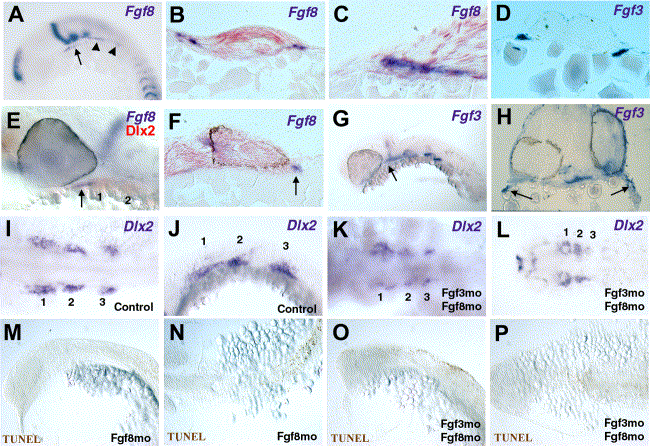
Fig. 6 Endodermal expression of Fgf8 during early crest migration and coexpression with Fgf3 in endoderm associated with the jaw. (A) At 16 hpf, Fgf8 transcripts are detected in first pouch endoderm (arrow) and endoderm (arrowheads) associated with posterior arches. (B, C) Transverse sections through an embryo at 16 hpf showing Fgf8 expression in endoderm associated with posterior arches (B; region indicated by arrowheads in A) and with anterior arches (C; high power view of one side of a section from the region indicated by arrow in A). (D) Transverse section through the second pharyngeal pouch of a 21-hpf embryo shows Fgf3 expressed by pharyngeal endoderm. (E?H) At 30 hpf, both Fgf8 and Fgf3 are expressed by endoderm associated with the developing jaw. (E) In situ hybridisation for Fgf8 (blue) and Dlx2 (orange) transcripts at 30 hpf. Fgf8 (arrow) is expressed in cells immediately anterior to the first arch (arches 1 and 2 are indicated). (F) Oblique section through the forebrain, eye, and anterior arch region of an embryo at 30 hpf showing Fgf8 transcripts in endoderm (arrow). (G) Fgf3 is expressed in endoderm associated with anterior arches (arrow). (H). Transverse section through a 30-hpf embryo showing Fgf3 expression in anterior endoderm. (I?L) Dlx2-positive neural crest cells are still present in embryos at 21 and 30 hpf following inhibition of Fgf3 and Fgf8 translation with morpholinos. The three neural crest cell populations are numbered. In situ hybridisation for Dlx2 transcripts in embryos at 21 hpf injected with a control morpholino (I, dorsal view; J, lateral view). Three Dlx2-positive neural crest populations are detected at 21 hpf following inhibition of both Fgf3mo and Fgf8mo (K; dorsal view); however, at 30 hpf, expression is reduced in the posterior population (L; dorsal view). (M?P) Cell death is not detected in migrating crest streams at 20 hpf following inhibition of either Fgf8 alone (M, N) or both Fgf3 and Fgf8 (O, P). (M, O) Lateral views and (N, P) dorsal views.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 264(2), Walshe, J. and Mason, I., Fgf signalling is required for formation of cartilage in the head, 522-536, Copyright (2003) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.