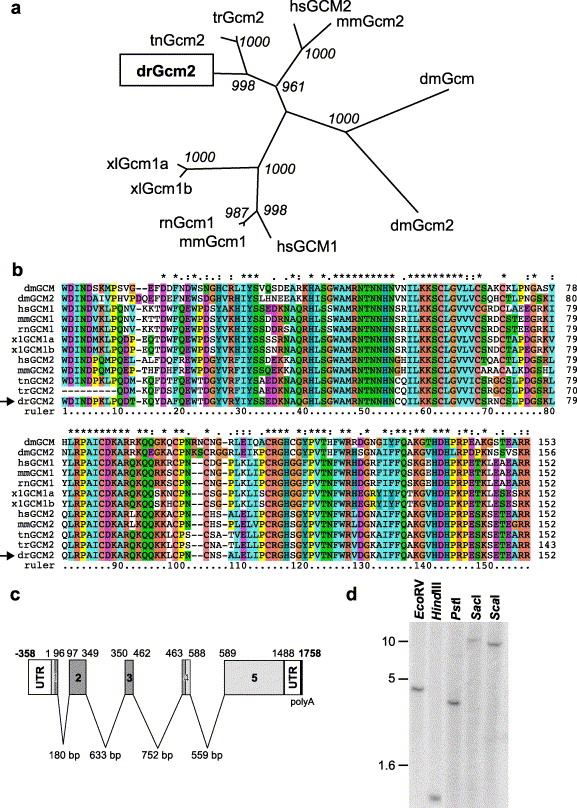
Fig. 1 Cloning of zebrafish gcm2. (a) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of Glial cells missing family members in alignment below (b). Danio rerio (zebrafish) gene is boxed and falls into the gcm2 clade. Bootstrap values are shown at nodes. Human (hs), Mouse (mm), Rat (rn), Zebrafish (dr), Fugu (tr), Tetraodon (tn), Xenopus (xl) and Drosophila (dm). (b) Multiple sequence alignment of Glial cells missing family members, spanning the DNA binding domain. Alignment was generated using the conserved DNA binding sequences only (from ?WDIND? to ?EARR? sequence). Danio rerio sequence is indicated by an arrow. (c) Depiction of the cDNA and genomic structure of the zebrafish gcm2 gene. Intron sequences were elucidated from the Sanger Centre trace sequence repositories and aligned contig sequences. Sequence analysis identified the start codon at 359 bp and identified an ORF of 1488 bp encoding a 496-amino acid protein. The gcm2 intron structure is conserved compared with the mouse and human genes, which also contain four small introns in the 52 coding sequence including sequence encoding the conserved N-terminal DNA binding domain, which spans the first four exons. The coding sequence is shown in light grey, the conserved DNA binding domain in dark grey, the untranslated region (UTR) in white and the polyA tail in black. (d) Genomic Southern blot using sequences corresponding to the gcm2 DNA binding domain as a probe. Restriction enzymes used are indicated and size bars indicate fragment size in kilobases.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 276(2), Hogan, B.M., Hunter, M.P., Oates, A.C., Crowhurst, M.O., Hall, N.E., Heath, J.K., Prince, V.E., and Lieschke, G.J., Zebrafish gcm2 is required for gill filament budding from pharyngeal ectoderm, 508-522, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.