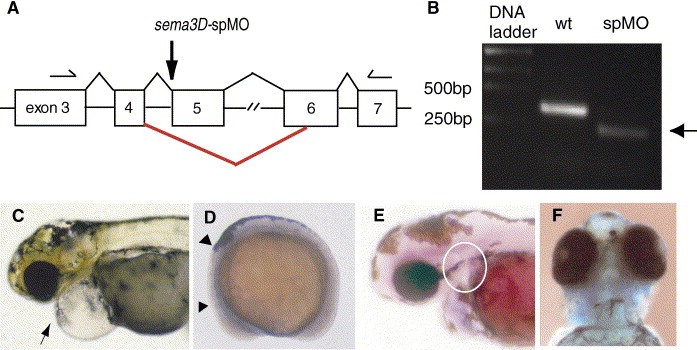
Fig. 3 sema3D-splice blocking morpholino knocks down sema3D mRNA and phenocopies sema3D-augMO. (A) Genomic structure of sema3D gene (GenBank #NM 131048), exons (boxes, not to scale). Splice donor site between 4th intron and 5th exon (5th exon codes amino acids in sema domain) was targeted by sema3D-spMO. The red line indicates the major splice variant observed following spMO injection. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis in B are shown as arrows (forward 5′-CCA GAC AAC ATC AAT AAA CAC CCC-3′, reverse 5′-TTG CCC AGG AAA TCA GAC GC-3′). (B) The single fragment (exons 3–7, 350 bp) amplified from wild-type RNA was diminished by sema3D-spMO and replaced by a smaller fragment (arrow, 230 bp). Sequencing revealed that sema3D-spMO caused utilization of cryptic splice sites, deleting exon 5 and part of exon 6, removing amino acids 129 through 168 (nucleotides 656–775 in sema3D mRNA), deleting the essential sema domain. Sema3D-spMO morphants had the same phenotypes as sema3D-augMO, including severe pericardiac edema (C, arrow, 4 dpf), reduction of crestin expression in cranial neural crest (D, arrowheads, 8 SS), reduction of rag1 expression in the thymus (E, white circle, 4 dpf) and loss of facial and pharyngeal cartilages (F, Alcian blue staining, 4 dpf).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 298(1), Sato, M., Tsai, H.J., and Yost, H.J., Semaphorin3D regulates invasion of cardiac neural crest cells into the primary heart field, 12-21, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.