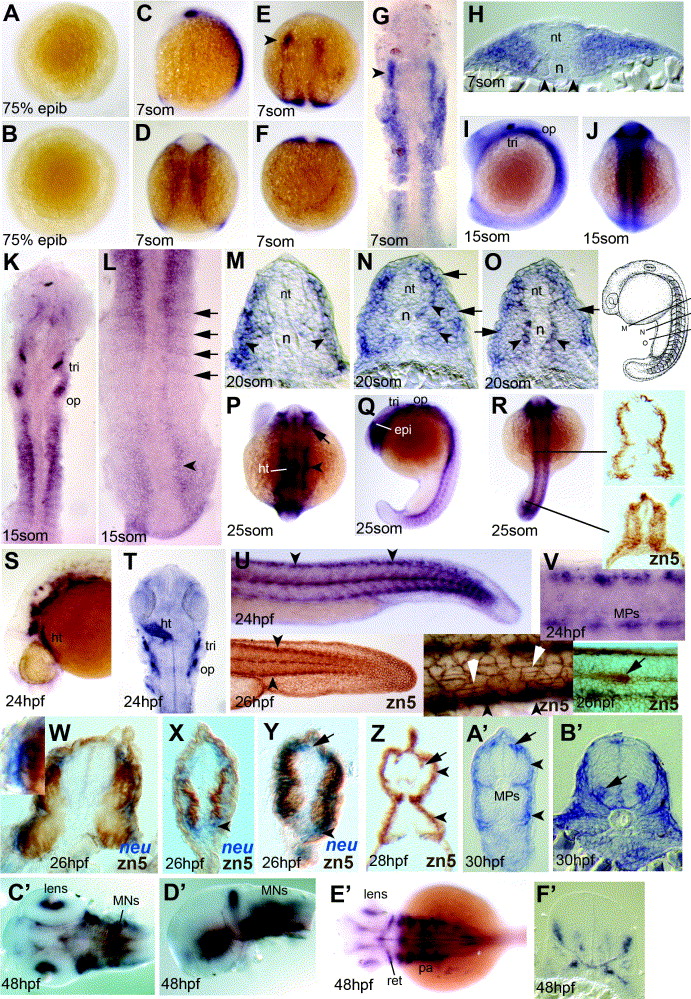
Fig. 4 Expression of neurolin and zn-5 antigen in zebrafish embryos up to 48hpf. (A and B) Lateral (A) and animal pole (B) views of embryo at 75% epiboly with no detectable signal. (C?H) Expression at 7 som viewed in wholemount (C?F; C lateral, E dorsal head, D dorsal trunk, F dorsal tailbud), dorsal flatmount (G) and trunk cryosection (H). The lateral region of anterior somites expresses neurolin (G and H), but adaxial cells do not (H, arrowheads). Lateral neural tissue of the head expresses, showing a markedly greater expression on the left (E and G arrowheads). (I?L) Embryos at 15 som in lateral (I), dorsal (J?L) wholemount (I and J) and flatmount (K and L) view. In anterior somites, signal extends more broadly lateral (I and K) compared to the posterior somites, where positive cells form single layers corresponding to somite borders and are also present in neural plate (L, arrows and arrowhead, respectively). (M?O) Serial cryosections of a wholemount neurolin-stained 20 som stage embryo at positions indicated in the schematic (modified from Kimmel et al., 1995). Slow fibre signal is present before, during and after migration (O, N, M, respectively, arrowheads). Expression is also present in lateral somite cells (M?O, arrows). (P?R) Dorsal (P and R) and lateral (Q) view of 25 som stage. Head expression includes retina, neural crest and heart (P; arrow, arrowhead and ht, respectively). The same embryo shows staining in the epiphysis, trigeminal and otic placodes (Q; epi, tri, op) and lateral mesoderm (R). Cryostat sections of wholemount zn-5-stained 25 som embryo at the indicated levels reveal transient zn-5 antigen throughout the nascent somite, becoming restricted to superficial cells in anterior smites (R, right). (S?V) 24 hpf embryos shown in lateral wholemount view of head (S) and tail (U), with flatmounts of head shown dorsally (T, ht heart) and the tail laterally (V). Clusters of cells in dorsal neural tube and 3?4 MP cells per somite at the dorso-ventral midline are evident (V). The zn-5 antigen labels similar cells in wholemount 26 hpf embryos (U, insets) including the dorsal and ventral somite extremes (black arrowheads, left and middle inset), the muscle pioneers, the superficial slow fibres (white arrowheads, middle inset) and the lateral line primordium (arrow, right inset). Note the lack of zn-5 antigen in Rohon?Beard neurons and posterior neural tube and the more marked antigen in lateral cell junctions within the ectoderm compared to the neurolin mRNA level. (W?Z) Dual wholemount staining for neurolin mRNA (blue, W?Y) and zn-5 immunoreactivity (brown, W?Z). Neurolin mRNA is present superficial to zn-5 stain (W, box magnified in inset; X,Y arrowheads). At 26 hpf, fast muscle contains zn-5 but no detectable neurolin mRNA (W and Y), slow muscle reacts strongly for zn-5 but has little neurolin mRNA (W?Y). Neurolin mRNA is detectable in Rohon?Beard neurons without zn-5 signal (Y, arrow). By 28 hpf, Rohon?Beard neurons react for zn-5 (Z, arrow) but fast muscle has lost zn-5 antigen. (A′ and B′) Cryosections of 30 hpf embryos in anterior trunk show staining in MNs in the ventral neural tube (nt) (B′, arrow). In mid-trunk region (A′), signal is in the dorsal and ventral superficial somite, muscle pioneer slow fibres and Rohon?Beard neurons (A′, arrowheads, MP and arrow, respectively). (C′?F′) Complex expression of neurolin in head and eye of 48 hpf embryos shown in dorsal (C′ and E′) and lateral view (D2) following dissection of head. Cryosection through the head at the region of ear (F2) shows small clusters of expressing cells, probably including cranial MNs of the ventral neural tube, neural entry/exit points and placodal cells. Abbreviations: epi, epiphysis; ht, heart; MPs, muscle-pioneer slow cells; op, otic placode; pa, pharyngeal arches; ret, retina; tri, trigeminal placode.
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 6(8), Mann, C.J., Hinits, Y., and Hughes, S.M., Comparison of neurolin (ALCAM) and neurolin-like cell adhesion molecule (NLCAM) expression in zebrafish, 952-963, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns