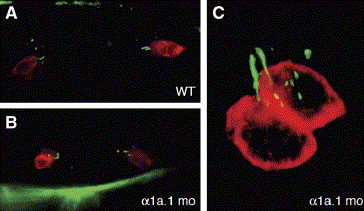
Fig. 7 Tether cells are present in α1a.1 morphant ears. Immunofluorescence was used to detect tether cell somae by labeling with HCS-1 (red) and tether kinocilia by labeling with anti-acetylated tubulin (green). (A) Lateral view of 24 hpf wild type (WT) otocyst. A pair of tether cells, each with a single kinocilium, is present at the anterior and posterior pole. (B) Dorsal view of α1a.1 morphant at 24 hpf. Two pairs of tether cells with kinocilia are visible. The tether cell pairs are closer together than in WT embryos due to the smaller size of the morphant otocyst. (C) Confocal image of α1a.1 morphant at 28 hpf. A pair of tether cells with kinocilia are located at the anterior pole of the otocyst. mo, morphant.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 294(1), Blasiole, B., Canfield, V.A., Vollrath, M.A., Huss, D., Mohideen, M.A., Dickman, J.D., Cheng, K.C., Fekete, D.M., and Levenson, R., Separate Na,K-ATPase genes are required for otolith formation and semicircular canal development in zebrafish, 148-160, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.