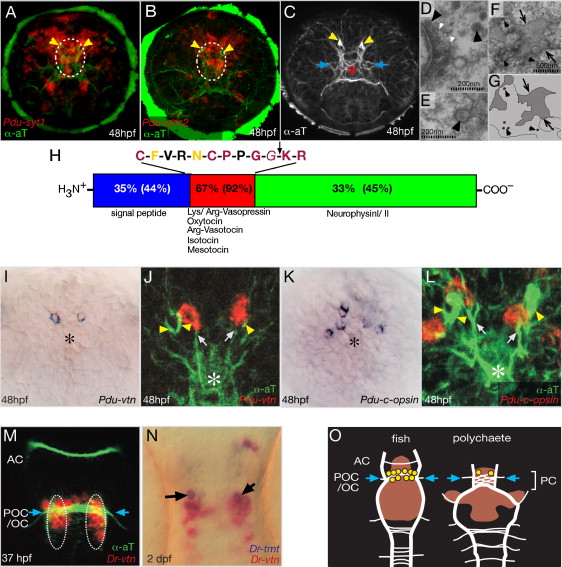
Fig. 3 Vasotocinergic Cells in the Developing Medial Neurosecretory Forebrain. (A?C) Differentiating neurosecretory cells in the Platynereis medial forebrain. Circles demarcate the location of the studied vasotocinergic and RFamidergic cells in comparison to axonal scaffold and position of sections shown in (D)?(F). (D?F) Transmission electromicrographs of the Platynereis medial forebrain plexus; black arrowheads, dense core vesicles (DCV); white arrowheads, synaptic vesicles (SV); scales as indicated. (D) Synapse containing DCV and SV. (E) DCV release, indicating larval neurosecretory activity. (F) Primary body cavity (black arrows) reaching into the plexus. (G) Scheme of (F). (H) Scheme of Platynereis-Vasotocin-Neurophysin (Pdu-Vtn), based on Figure S2. Percentages: identity of Mus ArgVasopressin-Neurophysin to Pdu-Vtn (in brackets: to zebrafish Vtn). Arrow demarcates the predicted cleavage site behind the nonapeptide. Different colors indicate the degree of conservation to other lophotrochozoans: complete (red), partial (yellow), none (black). (I?L) Pdu-vtn and Pdu-c-opsin expression localizes to the same landmarks (axons and large cilia of extraocular PRCs). (Note that these cells do not appear to bear the prominent cilia themselves.) Coexpression could not be assayed directly due to technical limitations (Tessmar-Raible et al., 2005). (M and N) Zebrafish vtn and tmt-opsin are coexpressed (arrows) by cells adjacent to the postoptic commissure/optic chiasm (blue arrows). (O) Summary schemes of zebrafish and Platynereis larval brains, indicating the position of vasotocinergic cells (yellow) with respect to the axon tracts (white) and nk2.1 expression (red). Anterior to the top. Blue arrows indicate positions of optic commissures (POC/OC). Stages, riboprobes, and antibodies as indicated. Asterisks demarcate the position of the neurosecretory forebrain plexus; yellow arrowheads, large cilia of deep brain photoreceptor cells; white arrows (J and L), projections of vtn+ cells into the plexus; blue arrows, entry of optic fibers into the axonal scaffolds of both Platynereis and zebrafish. (A?C and I?L) Apical view, ventral down; (M?O) ventral view, anterior to the top. AC, anterior commissure; POC/OC, postoptic commissure/optic chiasm; PC, preoral commissure. Depth of confocal reconstructions: (A) 31 μm, (B) 35 μm, (C) 30 μm, (J) 15 μm, (L) 18 μm.
Reprinted from Cell, 129(7), Tessmar-Raible, K., Raible, F., Christodoulou, F., Guy, K., Rembold, M., Hausen, H., and Arendt, D., Conserved sensory-neurosecretory cell types in annelid and fish forebrain: insights into hypothalamus evolution, 1389-1400, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Cell