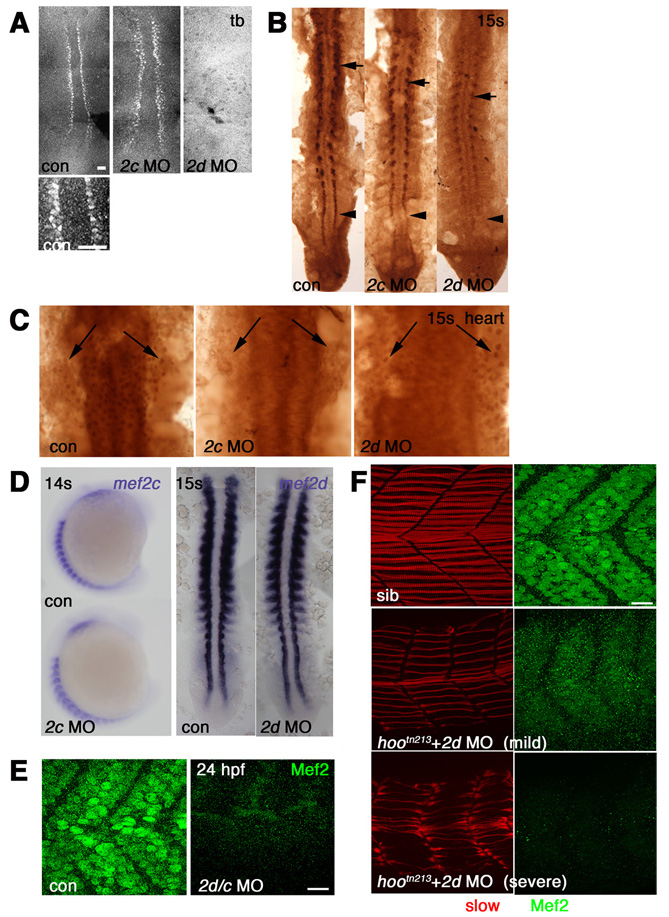
Fig. S1 Morpholino knockdown of Mef2s. Immunodetection with anti-Mef2 antibody visualized with fluorescent (A,E,F) or DAB staining (B,C) or in situ mRNA hybridisation (D) viewed in dorsal flatmount (A-C,D right; anterior to top), lateral wholemount (D left; anterior to top, dorsal to left) or lateral flatmount (E,F, anterior to left, dorsal to top). (A) Adaxial cells in presomitic mesoderm show nuclear staining that is abolished by injection of mef2d MO, but not mef2c MO. (B) At 15 somites, mef2d MO ablates adaxial expression (arrowhead) and reduces expression in differentiated slow fibres (arrows), whereas mef2c MO has little effect. Note that mef2d-specific MO had no effect on anti-Mef2c signal (compare to Fig. S2B). (C) Heart anlagen in midline beneath neural tube shows nuclear reaction (arrows) in control that is abolished by mef2c MO, but not by mef2d MO. (D) At 14-15 somites, neither mef2d nor mef2c MOs affect levels of the cognate mRNA. (E) At 24 hpf, Mef2 immunoreactivity present in fibre nuclei is abolished by mef2d/c MO. (F) Confocal stack of Mef2 immunoreactivity (green) and slow MyHC (red) in embryos from a hoover heterozygote cross. mef2d MO-injected embryos show three phenotypes: severely affected with no detectable Mef2 (bottom), mildly affected with weak Mef2 (middle), or indistinguishable from uninjected control embryos, all of which contain strong Mef2 and well-organised slow fibres (top). Scale bars: 20 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development