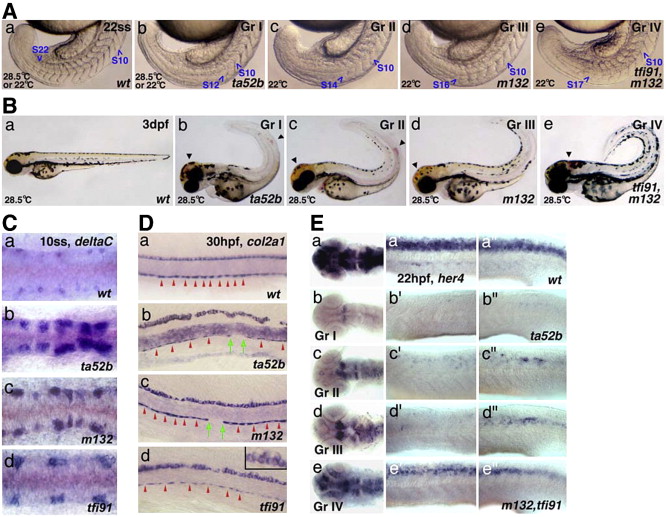
Fig. 1 Phenotypic severity of different mib mutants. (A) mib somite phenotype at 22ss. Somite 10 and last discernible somite are marked. See the text and Table 1 for the phenotypic grouping and mutant description of different genotypes. (B) 3dpf tail and pigment phenotypes. Arrowheads mark the hemorrhage sites. (C) Dorsal view of deltaC hindbrain reticulospinal neurons at 10ss. (D) Lateral view of midline phenotypes demonstrated by col2a1 expression at 30hpf. Obvious gaps (marked by green arrows) in mibm132 and mibta52b mutants and elongated cells in mibtfi91 mutants can be seen in hypochord, indicating a reduction in cell number (red arrowheads mark the boundaries of hypochord cells). mib floor-plate cells are less tightly packed and appear to be round and larger (insert in panel d) than in wt embryos and they are often dorsally displaced in mibta52b mutants. (E) WISH analysis of mib mutants by her4 at 22hpf, (a–e) head region, dorsal view; (a′–e′) trunk region; and (a″–e″) tail region around cloaca, both lateral view. All are head to the left, except head to the top in panel A.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 305(1), Zhang, C., Li, Q., Lim, C.H., Qiu, X., and Jiang, Y.J., The characterization of zebrafish antimorphic mib alleles reveals that Mib and Mind bomb-2 (Mib2) function redundantly, 14-27, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.