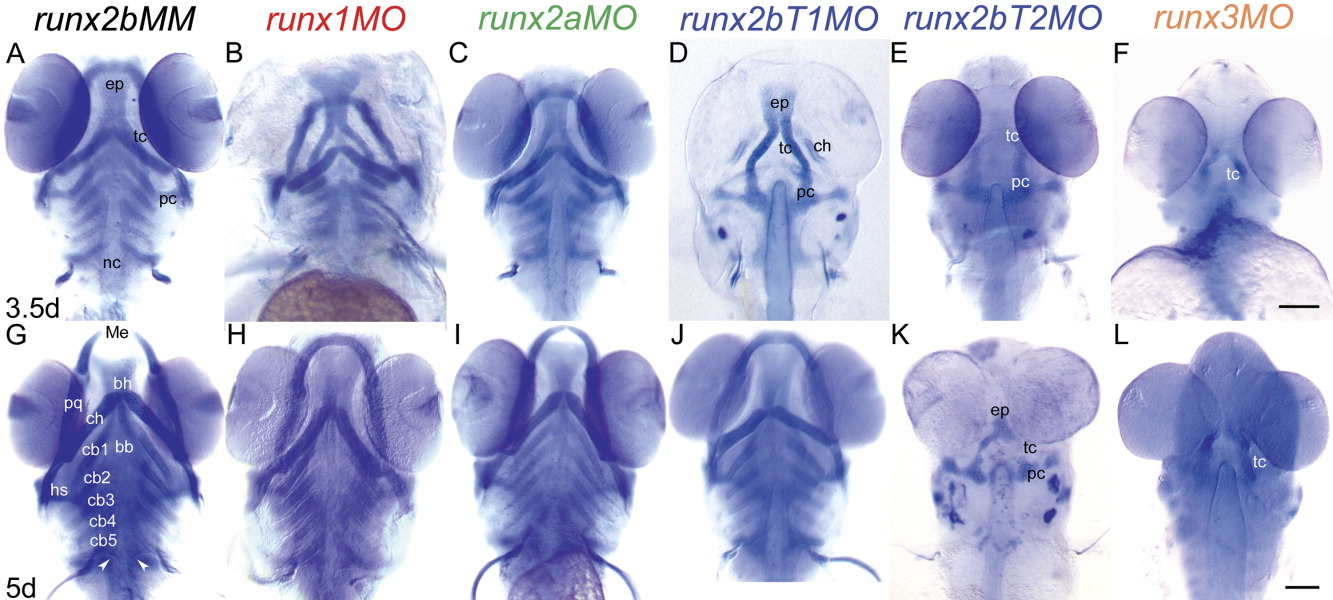
Fig. 4 Loss-of-function analyses using antisense morpholinos demonstrate which Runx proteins are essential at the onset of endochondral bone formation in the head skeleton. Embryos were injected with optimal amounts of MO at the 1-4 cell stage to inhibit gene function, and cartilage development was visualized with alcian blue staining at 3.5 (A-F) and 5 (G-L) dpf. (A,G) runx2bMM; (B,H) runx1MO; (C,I) runx2aMO; (D,J) runx2bT1MO; (E,K) runx2bT2MO; (F,L) runx3MO. Compared to runx2bMM controls, embryos treated with runx2bT1MO, runx2bT2MO, and runx3MO display significant reductions in chondrocyte differentiation at 3.5dpf (D-F). By 5dpf, runx2T1 morphants recover from an early delay in chondrogenesis (J), but those injected with runx2bt2MO and runx3MO show persistence of cartilaginous abnormalities with underdeveloped and reduced cartilage (K,L). The head skeleton of runx1 and runx2a morphants are mildly misshapen at 3.5dpf (B,C), and these become morphologically normal by 5dpf (H,I). Scale bars = 100 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.