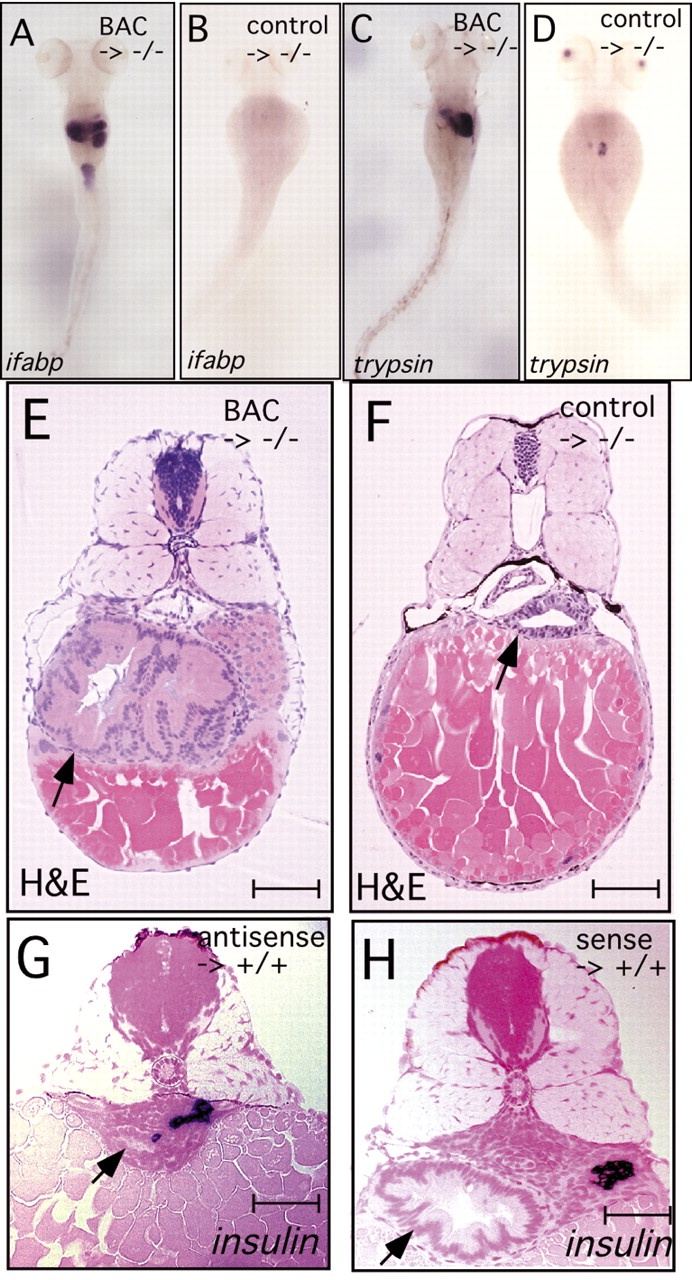
Fig. 5 Rescue and phenocopy of npo mutation. (A,C,E) 96 hpf npo-mutant embryos that had been injected with NotI-digested BAC 37b12 at the 1-cell stage. (B,D,F) Mutants injected with BAC 37b12 pre-cut with restriction endonucleases NotI and SnaBI, which cuts only between the first and second exon of the npo gene. (G,H) Wild-type embryos injected with morpholino oligonucleotides encoding antisense and sense sequences, respectively, from the npo transcript. (A,B) Representative embryos stained by whole-mount in situ hybridization for ifabp show rescue of this marker by BAC 37b12 injection in the expected mosaic pattern, and undetectable rescue observed using the cleaved BAC. By comparing panel A with Fig. 2E, we note that the BAC-injected mutant embryos have a broader ifabp expression pattern than the wild-type embryos. (C,D) Staining for trypsin demonstrates mosaic rescue of the npo phenotype, also with a broader expression pattern than seen in the wild-type (compare with Fig. 3C). The control-injected embryos shows a few cells stained for trypsin expression, which we also note occasionally in control-uninjected embryos. (E,F) Embryos shown in A and B, respectively, were sectioned and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. This revealed an over-expanded intestinal and exocrine pancreatic epithelium in the embryos injected with intact BAC 37b12, but no histological effect on the mutant phenotype in the control (arrows). (G,H) Histological sections of embryo injected with npo-specific morpholino oligonucleotides, sense or antisense as indicated, stained for insulin by whole-mount in situ hybridization, then sectioned and counterstained with nuclear Fast Red. Antisense injection leads to hypoplasia, dysmorphogenesis and abrogation of epithelial cytodifferentiation similar to that seen in the npo-homozygous mutant. insulin expression is not affected, as seen in the homozygous mutant. Normal digestive organs are seen in the sense control. Note, the effects on the digestive organs due to manipulation of npo expression often result in uncoupling of the AP axes of the neural tube from the digestive organs. For this reason, we chose internal landmarks in the digestive tract (i.e. islet or gall bladder) rather than neural tube or somite landmarks. Arrows indicate intestine. Scale bars: A-D, 200 μm; E-H, 20 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development