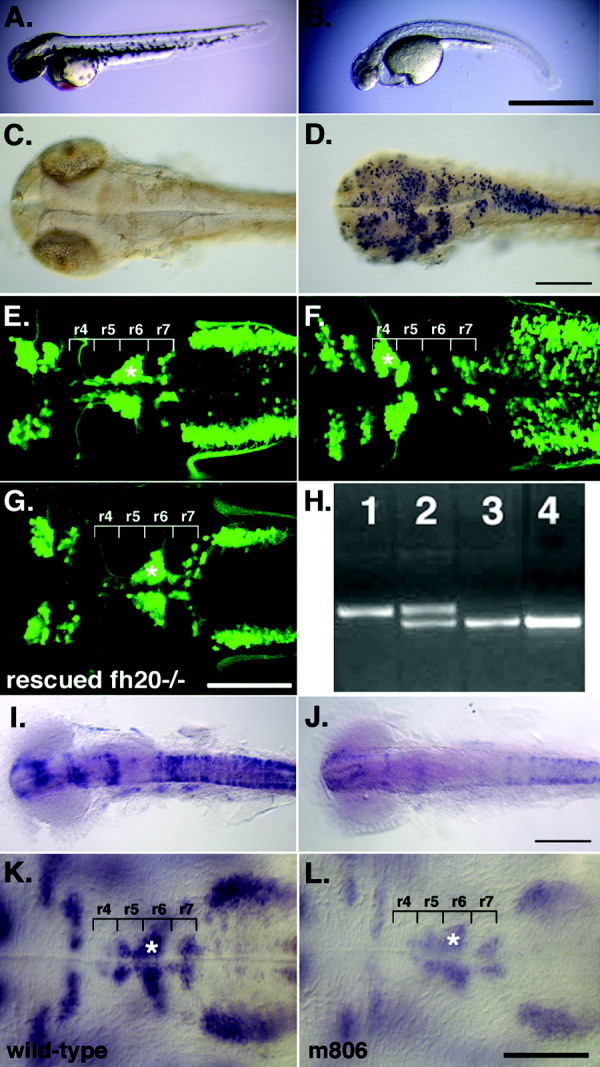
Fig. 1 A: fh20-/- mutant embryos exhibit multiple defects, including failure of facial branchiomotor neuron migration. Anterior is to the left in all panels. B: The morphological phenotype of fh20-/- embryos includes developmental delay and failure of tail elongation, absence of pigment formation, failure of the ventral retina to close, heart tube hypotrophy accompanied by pericardial edema, and degeneration of somites. C,D: The mutation is lethal at approximately 4 days postfertilization (dpf). Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridinetriphosphate nick end-labeling (TUNEL) labeling indicates that apoptotic cell death is increased in fh20-/- (D) compared with wild-type (C). E,F: Facial branchiomotor neurons (asterisks) fail to migrate posteriorly from r4 in isl1-GFP transgenic fh20-/- embryos (F) compared with wild-type (E). G: Full-length wild-type spt5 mRNA injected into fh20-/- embryos rescues facial branchiomotor neuron migration. H: Polymerase chain reaction genotypes for an absolutely linked microsatellite marker (30020R9) in (1) homozygous wild-type, (2) fh20+/-, (3) fh20-/-, and (4) the rescued fh20-/- embryo shown in G. I,J: In situ hybridization for ngn1 expression indicates a decrease in intensity that correlates with the fh20 mutation: wild-type (I) and fh20-/- (J). K,L: Facial branchiomotor neurons, identified by islet1 in situ hybridization, migrate normally in the m806 point mutant of foggy/spt5 that abolishes the negative effect on transcript elongation. Scale bars = 900 μm in A,B, 100 μm in C-L.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.