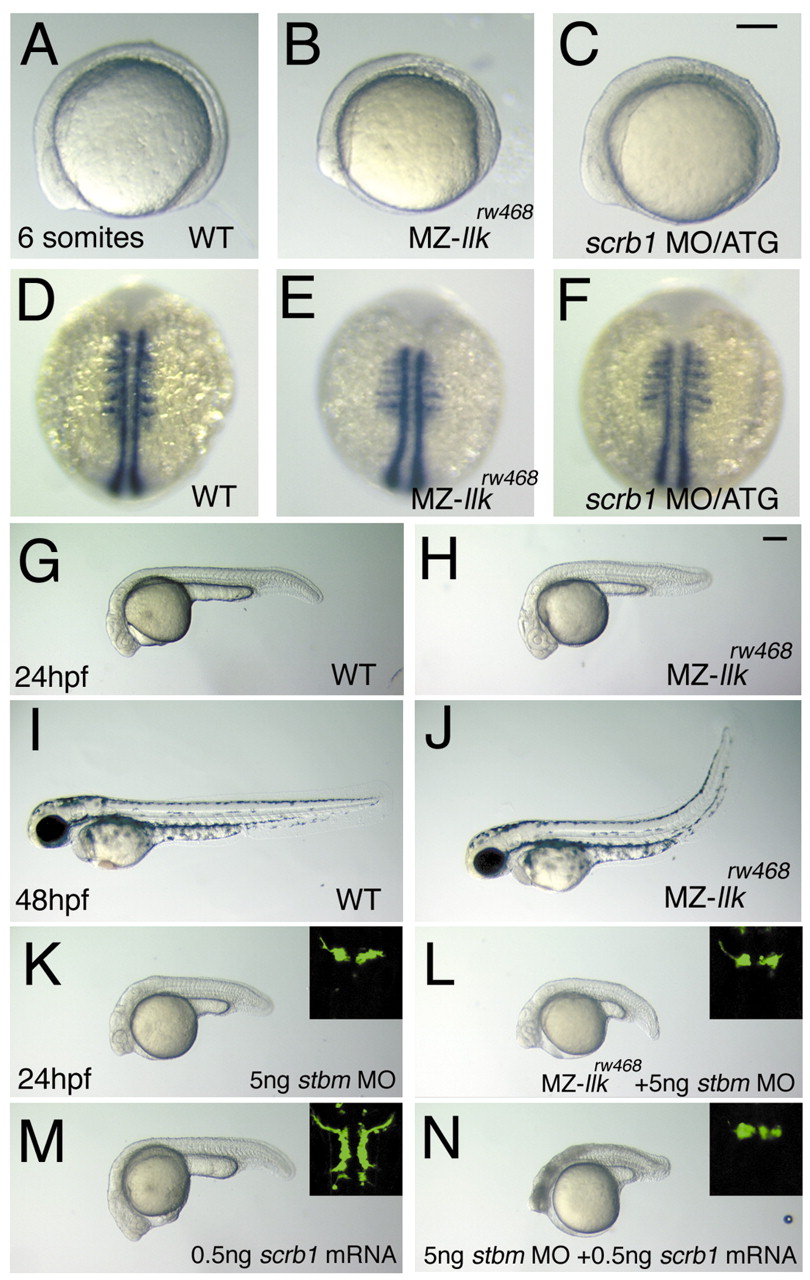
Fig. 8 Maternal llk/scrb1 is required for convergent extension movements and genetically interacts with tri/stbm. (A-F) Maternal and zygotic (MZ-) llkrw468 embryos show slight convergent extension (CE) defects. Wild-type (A,D), MZ-llkrw468 (B,E) and scrb1 MO/ATG-injected (C,F) embryos were observed when alive (A-C) or labeled with myoD RNA probe(Weinberg et al., 1996) (D-F). In MZ-llkrw468 and scrb1 MO/ATG-injected embryos, the anterior-posterior axis was shorter and somatic mesoderm wider than wild-type embryos. (G-J) Morphology of embryos recovered in the later stages; only tail regions are deficient in MZ-llkrw468 embryos (H,J; compare with wild-type embryos shown in G,I). (K-N) llk/scrb1 genetically interacts with tri/stbm. (K) Wild-type embryos injected with stbm MO show slight CE defects. (L) MZ-llkrw468 embryos injected with stbm MO had slightly greater CE defects. (M) Wild-type embryos injected with scrb1 mRNA had slight CE defects. (N) Wild-type embryos co-injected with stbm MO and scrb1 mRNA showed severe CE defects. (K-L) Images of the nVII motor neurons in each embryo are shown in insets. Scale bars: 100 Ám.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development