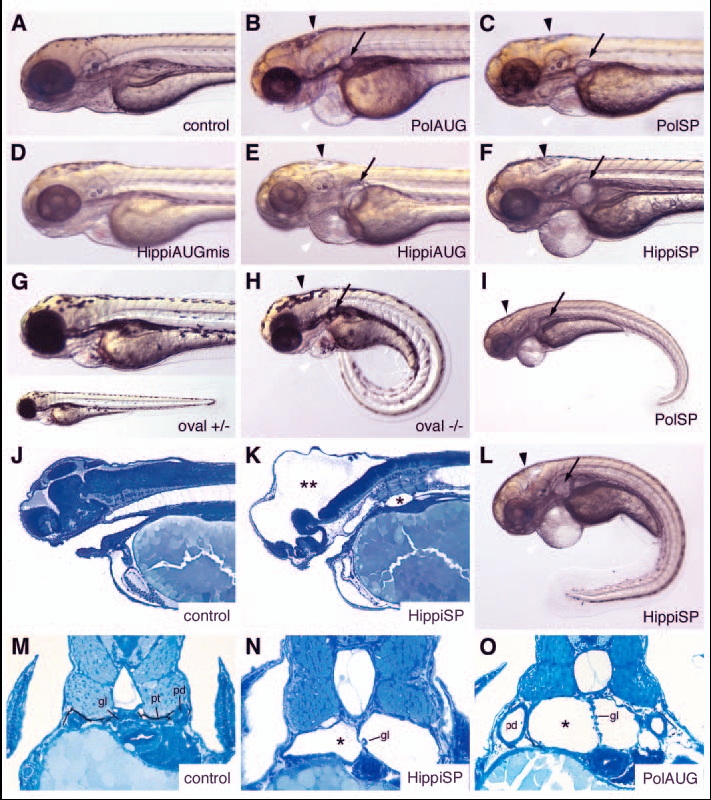
Fig. 3 IFT morphant phenotype: kidney cysts and hydrocephalus. Disruption of polaris function by injection of polarisAUG (B) and polarisSP (C,I) results in hydrocephalus (black arrowhead), pronephric cyst formation (arrow), pericardial edema (white arrowhead), and ventrally bent body axis at 72 hpf compared with non-injected control embryos (A). This phenotype imitates the oval homozygous mutant (H), in which the polaris gene is mutated. Heterozygous embryos are indistinguishable from wild-type controls (G). Embryos injected with the control hippiAUG mismatch morpholino have a normal morphology (D), whereas hippiAUG (E) and hippiSP (F) cause a phenotype similar to the polaris morphants and the oval homozygous mutant. (J) Wild-type embryo in longitudinal section. (K) hippiSP morphant embryo showing severe hydrocephalus (**) and kidney cyst (*). (L) hippiSP morphant embryo showing axis curvature, cysts (arrow) and hydrocephalus (arrowhead). (M) Histological cross sections of a 72 hpf control embryo show the midline fused glomerulus, pronephric tubules and pronephric ducts on either side. (N,O) hippiSP morphant embryos at 72 hpf show a cystic dilatation (*) of the pronephric tubules with a stretched glomerulus in the midline. (O) polarisAUG morphants show kidney cysts (*) and distension of the pronephric ducts. gl, glomerulus; pd, pronephric ducts; pt, pronephric tubules.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development