Fig. 3
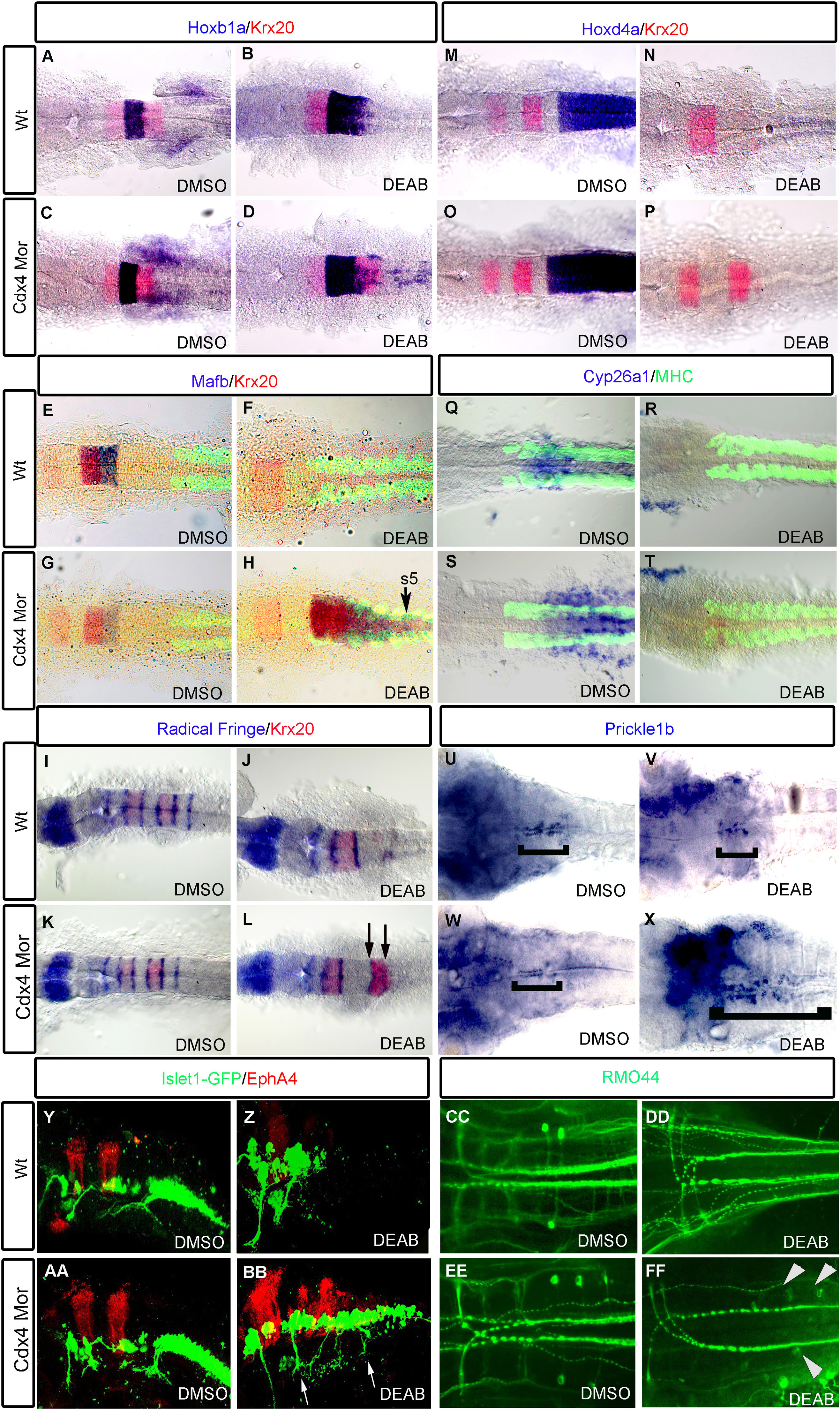
Knockdown of Cdx4 in RA-deficient embryos rescues the posterior hindbrain. hoxb1a expression in r4 is slightly expanded in RA-deficient embryos (B) compared to wildtypes (A) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (C). Expression of krx20 in r5; mafb in r5,r6; hoxd4a and cyp26a1 in r7/8 are lost in RA-deficient embryos (F, N, R) compared to wildtypes (E, M, Q) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (G, O, S). In RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos hoxb1a (D) expression is reduced, krx20 in r5 (D, H, L, P), mafb in r5,r6 (H) is rescued but hoxd4a (P) and cyp26a1 (T) expression in r7/8 is still absent. Six radical fringe (rf) bands marking rhombomere boundaries are found in wildtypes (I) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (K). Three rf bands are detected in RA-deficient embryos (J), while two additional bands, flanking krx20 expression in r5, return in RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos (L arrows). Prickle1b expression is in facial motor neurons of r4-6 in wildtypes (U bracket), cdx4 morphants (W bracket) and RA deficient embryos (V bracket). Prickle1b expression is expanded into the r7/8 position in Cdx4/RA double deficient embryos (X bracket). (Y-Z, AA, BB) Lateral view of hindbrain motor neurons marked by Islet:gfp and r3,5 marked with epha4. Branchal motor neurons in cdx4 morphants (AA) appear similar to wildtypes (Y). Vagal motor neurons of r7/8 are absent in RA deficient embryos (Z). Islet:gfp neurons return to r7/8 in Cdx4/RA double deficient embryos (BB arrows). RMO44 antibody marks reticulospinal neurons in wild-types (CC) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (EE). Mi and CaD are absent in RA-deficient embryos (DD) but return in Cdx4/RA deficient embryos (FF arrowheads). (A-P) are co-stained with krx20 (r3,r5) and (E-dH, Q-T) are co-stained with myosin heavy chain antibody (somites). All embryos are flat-mounted, (A-T) at 20 somite stage and (U-Z, AA-FF) at 48 hpf. (A-D) n=30/30, (E-H) n=15/15, (I-T) n=15/15, (U-X) n=20/20, (Y-Z, AA-BB) n=15/15, (CC-FF) n=13/15 per condition.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 410(2), Chang, J., Skromne, I., Ho, R.K., CDX4 and retinoic acid interact to position the hindbrain-spinal cord transition, 178-89, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.